A photo of a tiger.
Predatory Pricing
What is Predatory Pricing?
Predatory pricing or destroyer pricing, refers to the anti-competitive practice of setting the price of a product very low or below its cost in order to kick out competitors from the market. Predatory pricing is considered illegal in many countries because of its intention to reduce competition in the market. Once the competition is eliminated, the firms can raise their prices in order to gain profits. Predatory pricing is anti-competitive because it has the potential to reduce the number of competitors in the market.
The existing firms, the defendants of predatory pricing, argued that the practice of lowering prices is a normal business strategy to increase their sales and market share, not an intentional attempt to undermine the marketplace. This pricing strategy does not always bring positive results, as the predatory companies lose profits in the short run. And when they feel that the competitor is eliminated, they increase prices to gain more profit, which in turn increases the likelihood of the entry of new competitors.
Understanding Predatory Pricing
Price is the most flexible element of the marketing strategy, which firms can change quickly in order to achieve desired objectives. Normally, private firms aim to maximise profits and charge a price for their products that is consistent with this objective. However, firms can, sometimes, sacrifice short-run profits by using predatory pricing. The predatory intent here is to eliminate small and vulnerable firms from the market by selling the products at a price which is below it’s the average cost. The following diagrams illustrate the use of pricing for profit maximisation and predatory pricing.
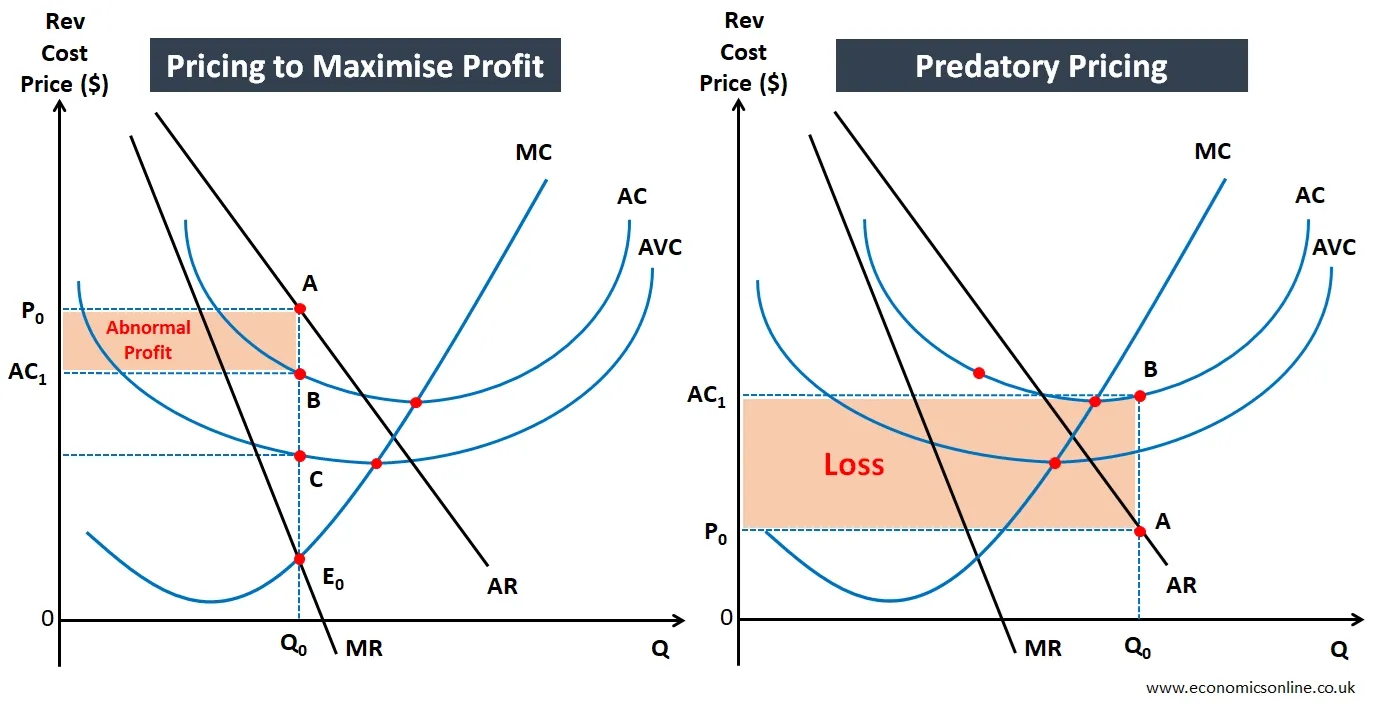
In the above diagram, the quantity is labelled on the horizontal axis (x-axis), while the vertical axis (y-axis) has revenue/cost/price. The graph on the left illustrates pricing for profit maximisation. This price belongs to the profit maximisation output which occurs when marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MR=MC). This price leads to an abnormal profit or supernormal profit as shown by the shaded area in the graph on the left. The graph on the right illustrates the use of predatory pricing, where price P0 is less than the average variable cost (AVC) and the average cost (AC), also called average total cost (ATC), leading to the loss for firm shown by the shaded area. Here, the firm using predatory pricing, is deliberately facing short run losses with an intention to gain more market power in the long-run, which may lead to even higher profits.
Effects of Predatory Pricing
The following are some effects of predatory pricing:
Short-Run Effects
The predatory pricing strategy benefits customers in the short-run. Due to price reduction, customers can buy the products at a low price which leads to an increase in consumer surplus, at least in the short run.
For the firm using predatory pricing, the loss is incurred in the short-run. However, for using this pricing strategy, the firm should have the ability to bear this short term loss through the availability of ample amount of funds.
For competitors, predatory pricing is a bad news. They have to reduce the price as well to remain competitive in the market. However, all the firms cannot sell their products in loss. Some firms are new, some are small and others lack funds to absorb the short run losses. These firms may end up leaving the market.
Long-Run Effects
In the long-run, after the elimination of competition, firms that used predatory pricing, increases the price of its products. Now, customers are negatively affected because they have to pay a higher price for the same product which they were buying at a lower price earlier. This harms the customer through a reduced consumer surplus in the long run. Moreover, the choice for consumers is also reduced due to the decrease in the number of substitutes previously made by the dead firms.
The firm, that used predatory pricing, will gain a high market power in the long term if the competition is successfully eliminated. This means that the price-making firm has an ability to increase prices. In this way, the seller will not only cover the short-run losses, but will also generate higher amount of profits in the long run. This will also make the demand for the products price inelastic, due to less number of substitutes. This means that the firm can increase the price of its products to increase total revenue and profits.
Reasons for Predatory Pricing
Why do firms use predatory pricing? Well, a simple answer is that predatory pricing practices are used by firms as a strategy to deal with the new firms that have entered the market. The entry of new firms may reduce the supernormal profits enjoyed by the incumbent monopolies, by taking some customers away from them. As a response, the firm in a monopoly market structure, may use predatory pricing to bear the temporary loss through prices set below the average cost of products. These low prices will make the new firms leave the market, as they may not have enough finance to absorb that loss. After the elimination of competition, the firm can regain its monopoly power and raise prices again. The use of predatory pricing by a monopoly may inculcate the fear in the minds of new firms and may become an entry barrier, which makes the entry of new firms difficult in an already less competitive market.
Another reason may be that the firm is trying to overcome sales crises or boost demand during times of economic instability. Businesses used strategies of discounts and other offers to enter the market for a new product or service and generate sales. Companies have to keep their prices low because their target audience is more price-sensitive, even when there are economic downturns. Unknown products can be known in the market with the help of this strategy.
Predatory pricing is also used by firms in the form of dumping, in which they try enter the foreign markets with unfairly low prices and try to eliminate the local firms there.
Companies Accused of Predatory Pricing
There are many examples of predatory pricing. Walmart is one of those companies accused of predatory pricing cases in 1993. The judge ordered that retailer to stop selling beauty products, health products, and drugs that cost less than fair market value. Three stores located in Conway and Arkansas accused Walmart of predatory pricing, as it is undercutting them to kick out other stores from business or marketplace.
Dumping as Predatory Pricing
Dumping is the practice of selling a product in a foreign market below its cost or below a fair market value. This strategy is used by international players and big organisations to dominate foreign markets. In the process of dumping, companies sell products cheaper in the foreign market as compared to their homeland. A continuously emerging global marketplace has added a new risk to those who attempt to dump goods. They bought some dumped goods abroad and then shipped them back to their country to sell them at high prices.
In the 20th century, dumping was seen in the case of the German Cartel, which controlled the European market for bromine, a main ingredient in many medicines and also important in photography. Then, when an American company called Dow Chemical started exporting high-quality bromine to Europe, the Germans retained their sales by exporting bromine to the U.S. at a price below their manufacturing costs in order to eliminate competition. Dow then simply buys bromine at dump prices and sells it in Europe at profitable prices, allowing Dow to retain its European customer base at the expense of the German Cartel.
Predatory Pricing and Law
The prosecutors of predatory pricing are trying to prove that low prices affect competitor businesses working independently in the marketplace, which is not good and also illegal. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) said that it carefully examines all the allegations of predatory pricing, but they are doubtful of such claims. The United States Department of Justice (DOJ) also said that predatory pricing is a serious problem and has to be resolved as soon as possible.
In general, a bar has been set on antitrust claims. The U.S. Supreme Court also said that predatory pricing not only affects the pricing practices of rivals but also affects competition in the marketplace.
Predatory Pricing and Public Interest
The use of predatory pricing increases the market dominance of a monopoly, and this may go against the public interest. Powerful monopolies can charge higher prices and restrict output and choice for consumers. This reduces their consumer surplus and, hence, their welfare. However, in the short run, general public benefits from low prices.
Pros of Predatory Pricing
The following are some pros of predatory pricing:
Large Market Share
Companies took advantage by using predatory pricing to keep their prices low, which are below the manufacturing costs of their competitors, which gives them a large market share. This large market share leads to economies of scale, low manufacturing costs, and high profit for a long period of time.
Less Competition
The predatory pricing strategy restricts new potential competitors from entering the market, as they know that this barrier to entry is caused by the predatory pricing strategy. This increases the market power of the dominant firms and reduces the contestability of the market.
Cons of Predatory Pricing
The following are some cons of predatory pricing:
Short-Term Financial Losses
A con of predatory pricing is the short-term financial loss. This is because price is set below the manufacturing cost, which leads to losses and strains financial resources.
Price War
If the competitors sustain the price-cutting phase, they can encounter price cuts, and then there will be a price competition affecting all the market participants.
Risks of Predatory Pricing
Predatory pricing is not an easy strategy to use and do involve some risks. For example, if a small town has many gasoline stations. But a petrol station can attract more customers or generate more business by keeping their prices relatively low. In order to kill competition, it is hard to sustain low prices for a long period of time. If this strategy works, it can only be achieved if the profit margin is large enough to quickly cover the losses. But when a sole petrol station increases its prices to normal, competitors grab the opportunity and enter the market again.
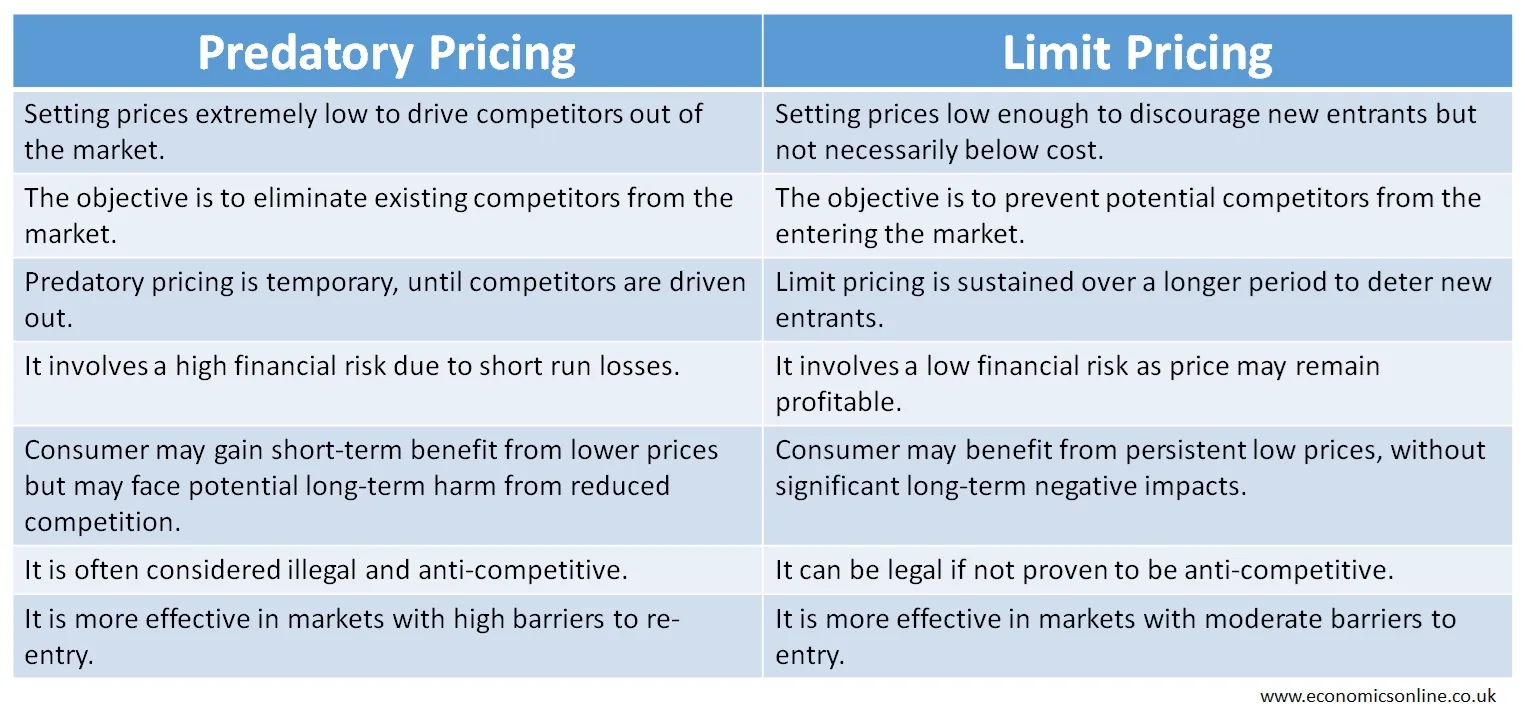
Predatory Pricing vs. Limit Pricing
As explained earlier, predatory pricing involves selling a product at a low price in order to reduce existing competition. On the other hand, limit pricing is the strategy of selling the products at low prices in order to stop new entrants from entering the market. Predatory pricing reduces existing competition, while limit pricing reduces potential competition. The following table contains the main points of difference between predatory pricing and limit pricing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, predatory pricing is a business strategy in which prices are kept below manufacturing costs in order to eliminate competition. Eliminating competition creates a situation of monopoly where a single firm dominates the market. This below-cost pricing strategy is considered illegal because it directly attacks the price points, resulting in the competitor firm losing its position in the market and leaving the market.


