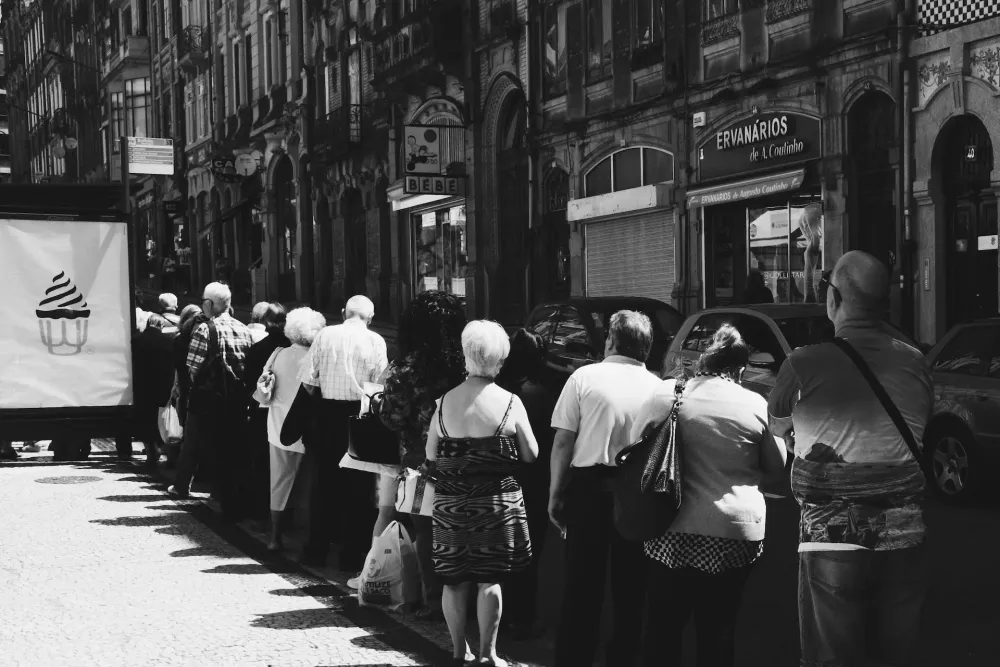
An image of people in line.
Shortages in Economics
Introduction
In free markets, resources are allocated by using the forces of demand and supply without any government intervention. These markets operate in equilibrium, a situation where the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied, as shown in the diagram below.
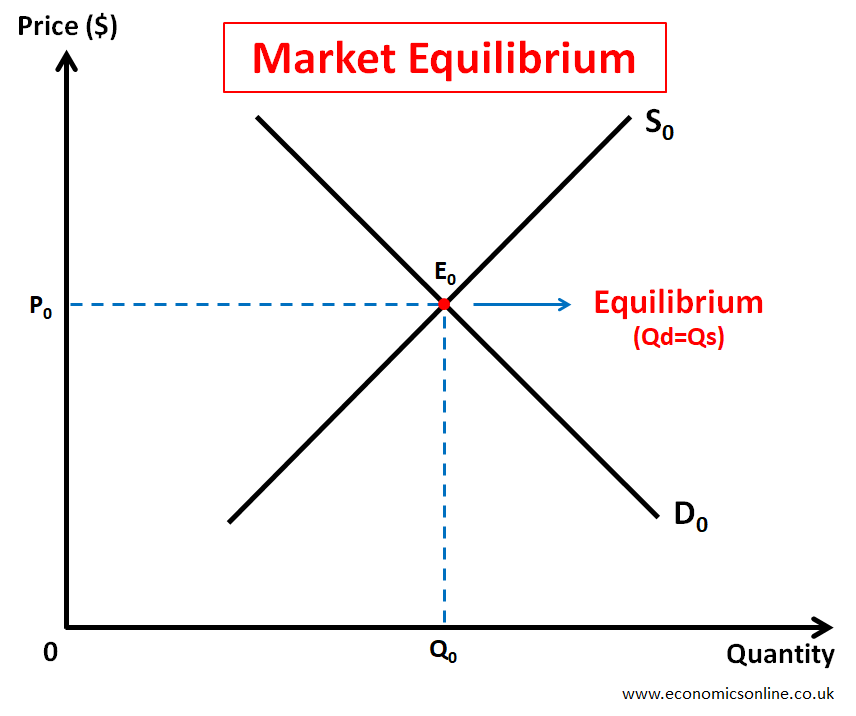
In the above diagram, market equilibrium is illustrated by point E0, where the demand and supply curves intersect, leading to the equality of quantity demanded and quantity supplied (Qd=Qs). This happens at price P0, which is the equilibrium price or market clearing price, while Q0 is the equilibrium quantity.
These free markets are self-correcting without any need for government intervention. However, market disequilibriums occur due to various reasons in the form of shortages and surpluses. In this article, we will discuss market shortages in detail.
What is Market Shortage?
A market shortage refers to a situation in the market when the quantity demanded of a product is greater than the quantity supplied. In other words, there is an inadequate supply of products, which is not enough to meet demand. In any market shortage, the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied (Qd>Qs). This is illustrated by the following diagram.
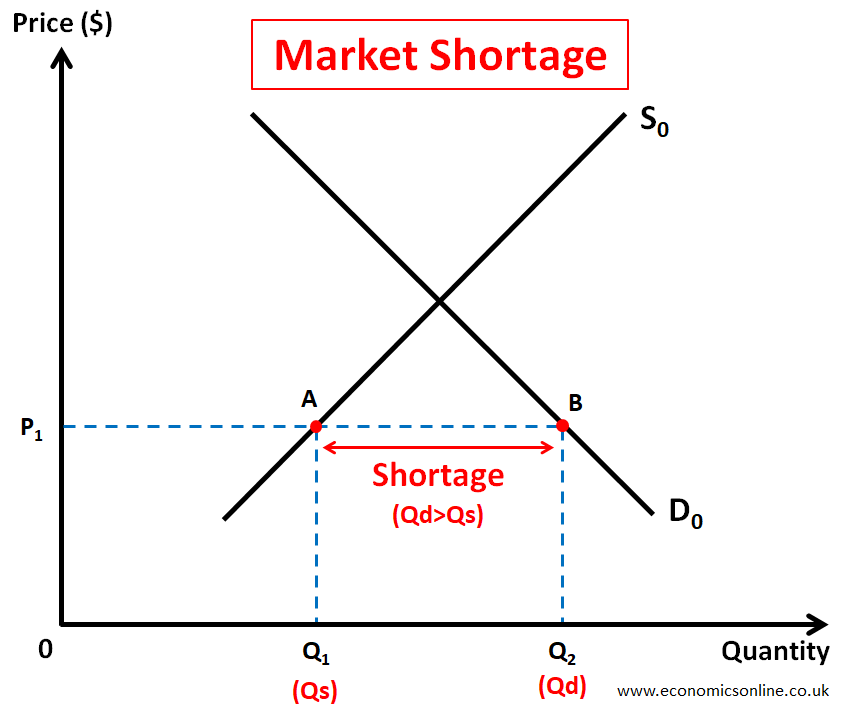
In the above diagram, at price P1, there is a market shortage equal to AB or Q1Q2. At price P1, the quantity supplied Q1 is given by point A, which is on the supply curve S0, while the quantity demanded Q2 is given by point B, which is on the demand curve D0. Q2 (Qd) is greater than Q1 (Qs) at price P1, leading to a market shortage. This is a state of market disequilibrium and can happen due to various reasons.
Market Surplus
Market surplus refers to a situation in the market when the quantity supplied of a product is greater than the quantity demanded. In other words, there is an inadequate demand for a product, which is not enough to clear the available supply. In any market surplus, the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded (Qs>Qd). This is illustrated by the following diagram.
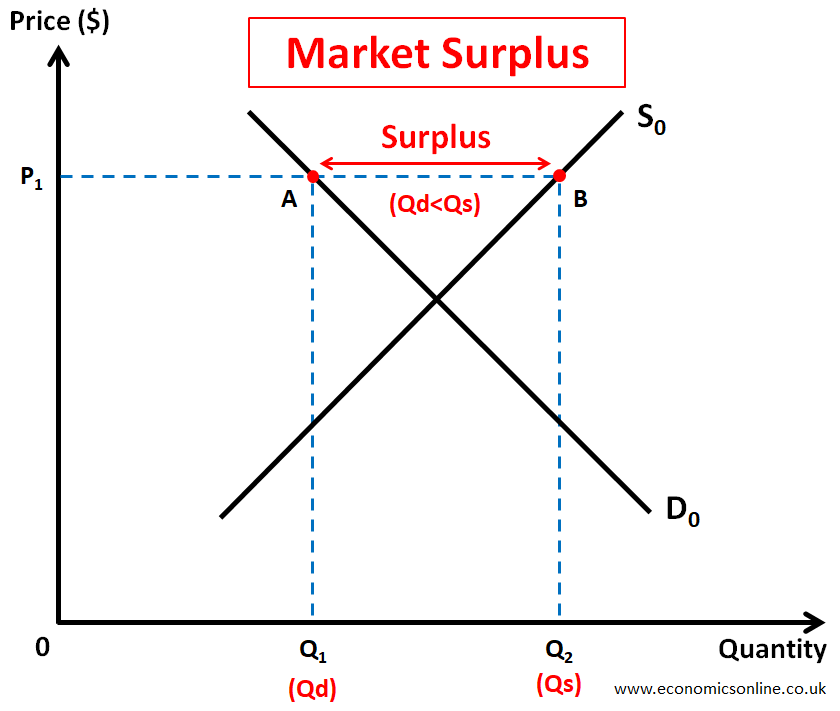
In the above diagram, at price P1, there is a market surplus equal to AB or Q1Q2. At price P1, the quantity demanded Q1 is given by point A, which is on the demand curve D0, while the quantity supplied Q2 is given by point B, which is on the supply curve S0. Q2 (Qs) is greater than Q1 (Qd) at price P1, leading to a market surplus. This is also a state of market disequilibrium and can happen for various reasons. A summary of the comparison between market shortage and market surplus is given in the form of a table later in this article.
Market Shortage - Example
Many market shortages occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic. There were shortages of beds and medical aids in the hospitals, as well as a shortage of morgues because they were full of dead bodies, and the ratio of people dying from COVID-19 broke records. During natural disasters or pandemics like COVID-19, shortages occur due to a sudden rise in the demand of various products, which cannot be satisfied by the existing supply of products. Markets are not normally prepared for the pressure of a sudden rise in demand or a supply shock because these types of events cannot be predicted or predetermined.
Causes of Market Shortage
The following are some major causes of market shortage:
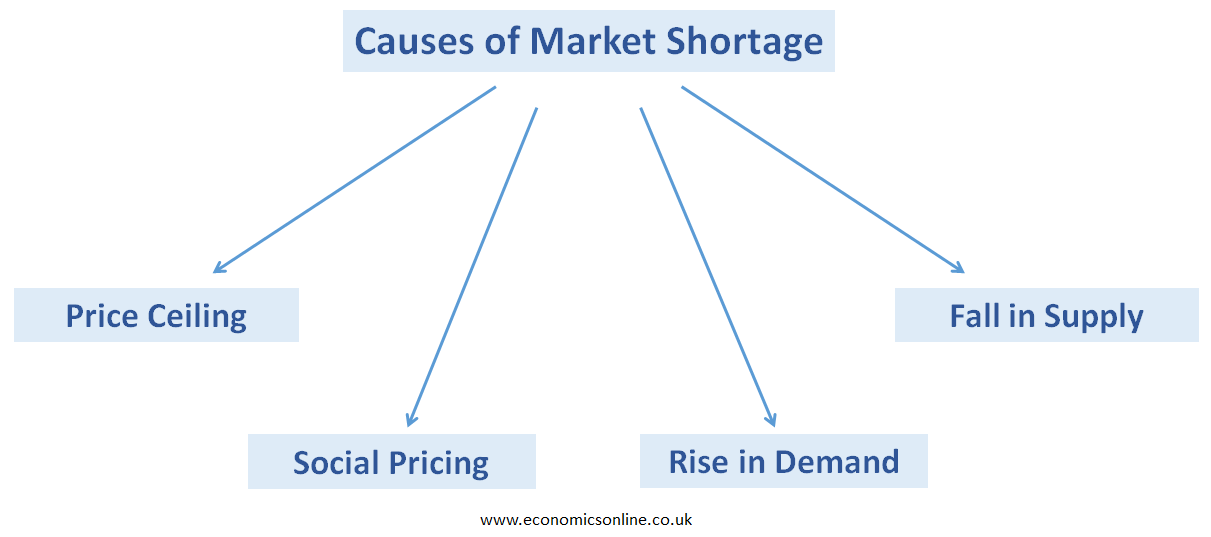
Price Ceiling
The price ceiling refers to the maximum legal price of a product. This maximum price is used by the government to control the prices of various products and is a major cause of market shortages. This is illustrated by the following diagram.
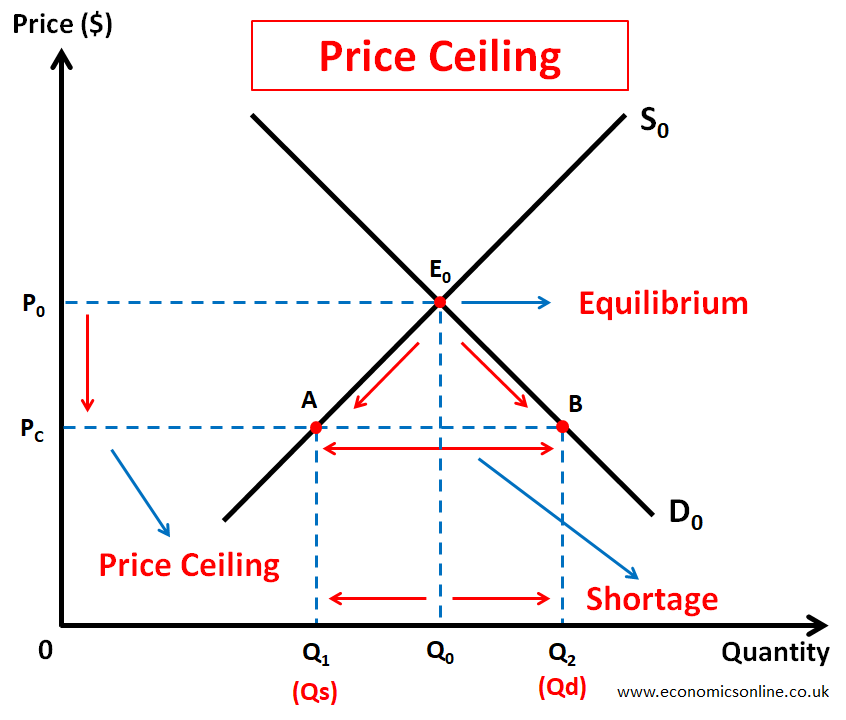
In the above diagram, initially, before using the price ceiling, the market was in equilibrium at point E0. The equilibrium price was P0, and the equilibrium quantity was Q0. The government believed that the price of P0 was too high and should be controlled. Hence, the government used the maximum price or price ceiling Pc. This makes any price above Pc illegal. Hence, the market cannot operate at P0. Due to the price ceiling, shortage AB occurred at price Pc as the quantity demanded (Q1) became greater than the quantity supplied (Q2).
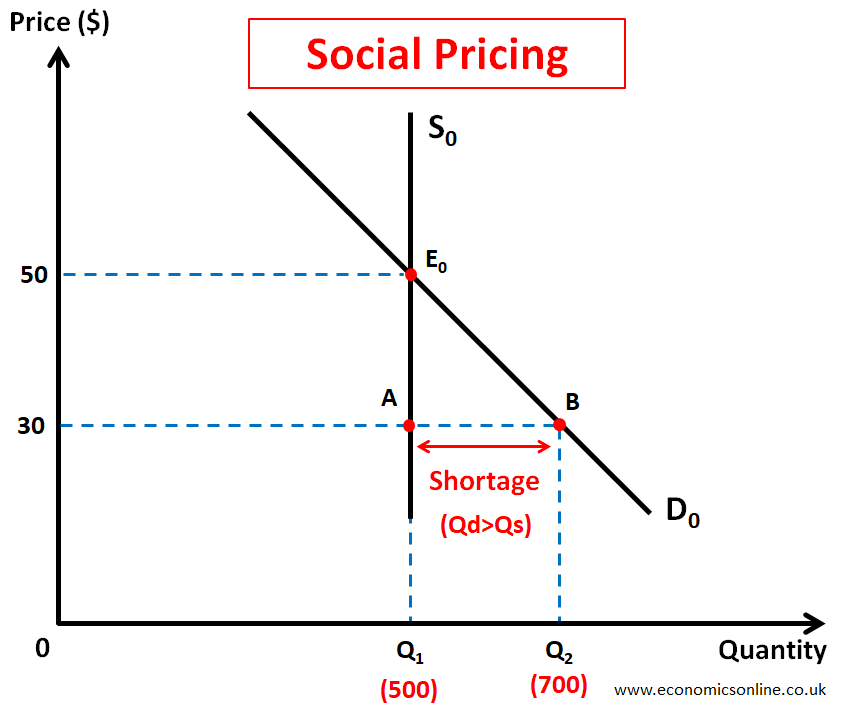
Social Pricing
Community clubs bring huge benefits to local communities, including better health and social cohesion. These community clubs, such as a local sports club, may set a lower price to avoid profiteering. Instead of setting the price of $50, a lower price of $30 is set, which has created a market shortage. This is illustrated by the following diagram.
Rise in Demand
A sudden rise in demand for a product can lead to a market shortage. This is illustrated by the following diagram.
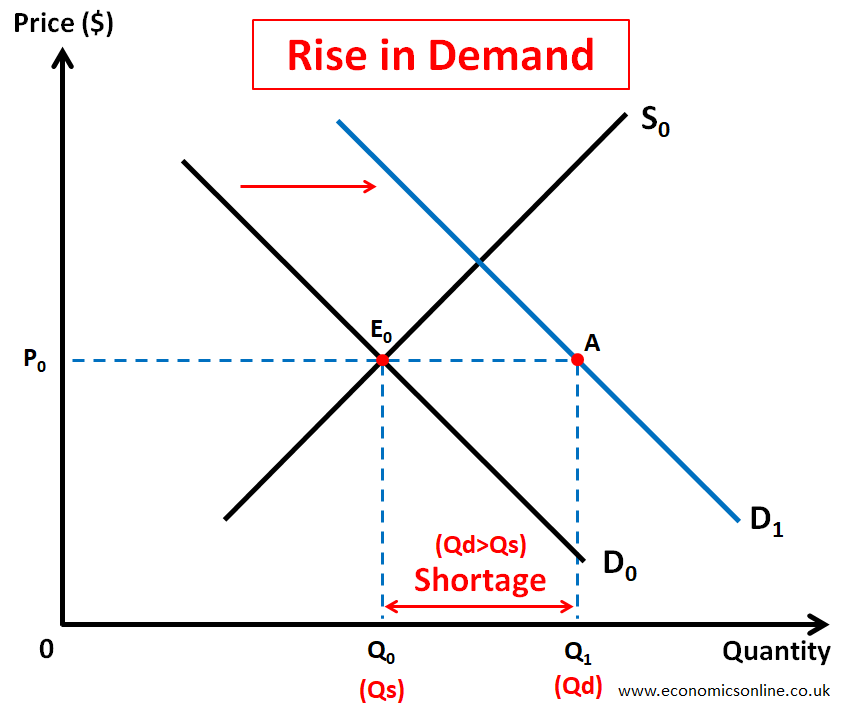
In the above diagram, initially, the market was in equilibrium at point E0. The equilibrium price was P0, and the equilibrium quantity was Q0. Due to a sudden rise in the demand for product from D0 to D1, a shortage E0A occurred at price P0 as the quantity demanded (Q1) became greater than the quantity supplied (Q0). Some examples of such market shortages are:
- Shortage of airline tickets due to a rise in their demand when schools are closed for vacations.
- Shortage of stationary items when the schools reopen after holidays.
- Shortage of warm clothes due to unusually cold weather.
- Shortage of tickets for a football match or a popular movie.
Fall in Supply
A sudden fall in the supply of a product can lead to a market shortage. This is illustrated by the following diagram.
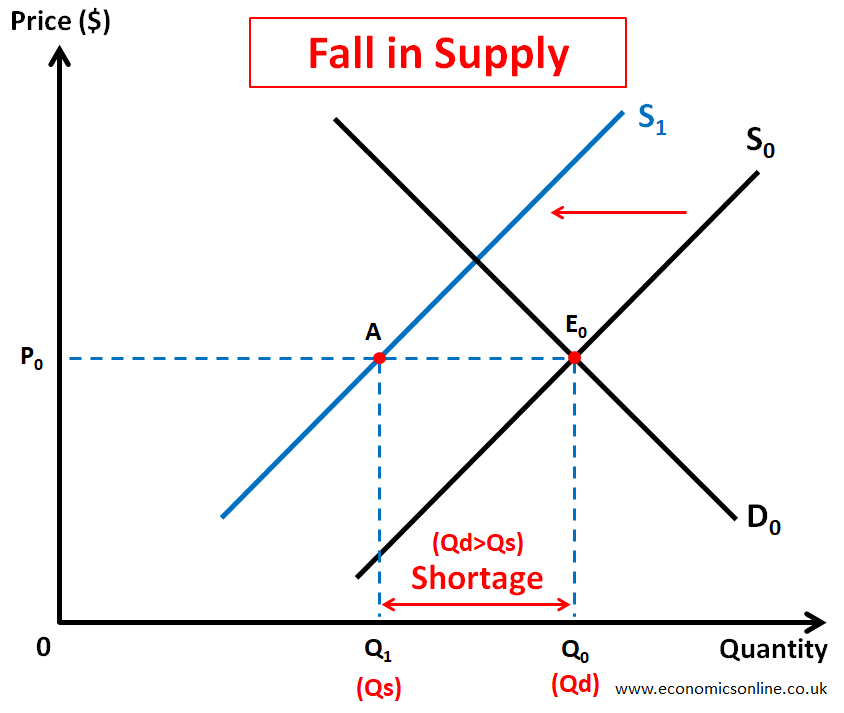
In the above diagram, initially, the market was in equilibrium at point E0. The equilibrium price was P0 and the equilibrium quantity was Q0. Due to a sudden fall in the supply of product from S0 to S1, a shortage E0A occurred at price P0 as the quantity supplied (Q1) became less than the quantity demanded (Q0). Some examples of such market shortages are:
- Shortage of agricultural products due to floods.
- Shortage of electricity due to a major system breakdown in power generation.
- Shortage of natural resources such as coal and gas because they are depleted.
Natural resources such as coal and gas, if depleted, can cause a permanent shortage of that particular resource. Natural resources are used in the manufacturing of certain products. If a shortage of a natural resource that is used to produce a product occurs, then there is a shortage of that product for a long period of time until and unless we can find an alternative for that.
Examples of Market Shortage
The following are some examples of market shortage:
Fuel Shortage
Many countries import fuel for running their economies. Any reason due to which fuel cannot be imported can create shortage of fuel. This shortage can be due to a war situation when the borders are closed, a global pandemic like COVID-19 disrupting the supply chain, lack of funds for importing fuel or a refusal of an oil exporting country to supply fuel.
Labour Shortage
Labour shortages occur when a country does not provide job opportunities to its citizens. They have to move to another country to seek job. Then a country has labour shortages due to limited resources for its citizens to earn and stay in their homeland.
Food Shortage
Food shortages occur when a natural disaster happens in a country, such as a flood, earthquake, etc. There is a limited availability of food, water, shelter, medical aid, and other necessities for living.
Electricity Shortage
Electricity shortages occur when there is an insufficient amount of electricity produced due to a limited availability of resources. This amount of energy can’t fulfill the demands of consumers. For example, governments do not focus on building the dams for storage and consuming the water for energy production.
Housing Shortage
Housing shortages occur due to the increasing population of the world. Due to an immense increase in population, there is a shortage of housing spaces for the construction of new houses. It also occurs when there are high construction costs charged by the buyers. Due to this, consumers can’t afford the housing costs. In this way, housing shortages occur.
Advantages of Shortages
The following points explain the advantages of the shortages:
Encourages Innovation
An important advantage of shortages is that they encourage innovation in the industry. Businesses and individuals are encouraged by the shortages that happen in the marketplace. They focus on innovating new products or services that can overcome the shortage. They try to innovate solutions or strategies to overcome the shortages.
Promotes Efficiency
Shortages encourage individuals to use the available resources wisely. Because when there is limited availability of resources, we should use them effectively and wisely. The limited availability of resources allows firms to enhance their efficiency and seek effective allocation of resources.
Reduces Inflation
A shortage occurs at a price which is lower than the equilibrium price. This means that, at least, some customers get the product at a lower price leading to a lower cost of living. This is especially true in case of an effective price ceiling. This may contribute to a reduced inflation at least in the short run.
Disadvantages of Shortages
The following are some points of disadvantage of shortages:
Waiting lines or Queues
A shortage means the excess demand for a product. This higher demand can lead to waiting lines or queues where customers are waiting for their turn to buy the product. The greater the shortage, the longer the waiting lines. The waiting time of customers is an unproductive use of their time as they may otherwise be doing something productive and useful. This is a major disadvantage of market shortage.
Black Markets
During a shortage, some customers cannot wait for their turn to get the product and may decide to buy that product from unofficial black markets. These markets do unrecorded and unregistered trading activities which give rise to underground, hidden or shadow economy.
Increased Demand for Substitutes
A shortage of electricity may mean that customers look for a substitute like solar panels leading to their increase demand. However, substitutes may not be perfect and some products may not have substitutes like a life-saving drug.
Economic Impact
Economies can be badly disturbed due to shortages because they lead to an increase in the prices of necessary goods due to limited availability. Consumers could not buy those expensive products. In this way, shortages negatively affect the economy of a country.
Social Consequences
There are also social consequences that a country has to face due to shortages. Due to an increase in population, there is a situation of social unrest due to the shortage of basic necessities of life.
Market Response to Shortages
Free markets are self-correcting and the price mechanism works to overcome the shortage. This is illustrated by the following diagram.
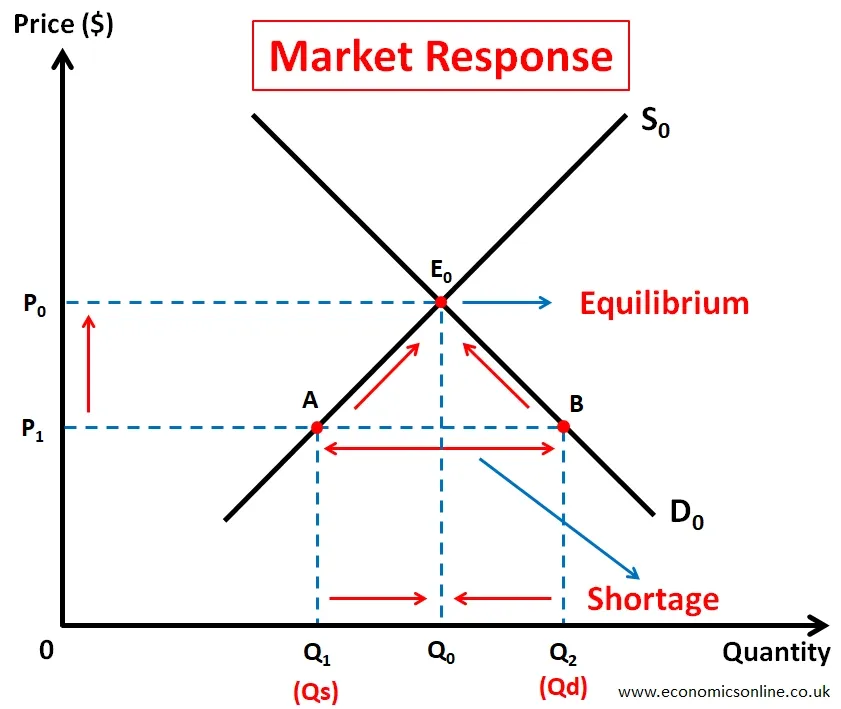
In the above diagram, at price P1, there is market shortage equal to AB or Q1Q2. The market mechanism will respond in the following ways to overcome shortage.
- Price will increase from P0 to P1.
- Due to an increase in price, sellers get incentive to supply more. Hence, the quantity supplied will increase from Q1 to Q0 according to the law of supply and there will be an extension in supply from point A to point E0.
- Due to an increase in price, buyers will buy less quantity of the product. Hence, the quantity demanded will increase from Q2 to Q0 according to the law of demand and there will be a contraction in demand from point B to point E0.
- Market shortage will be removed and the equilibrium will be restored at E0, P0 and Q0.
How to Overcome Shortages?
The following solutions are used to overcome shortages:
Increasing Production
When there is high demand for goods or services due to shortages, firms can increase the production of those demanded goods or services to tackle this situation. The increased production of necessary goods or services like wheat, sugar, etc. can lead to the solution of shortage.
Importing Goods
When shortages occur in a country, there may be a need of importing goods from other countries to fulfill excess demand. Importing goods from other countries to domestic country can be a good solution for shortages provided that the country has sufficient funds for imports.
Rationing Systems
A rationing system can also be used to overcome the shortages. The governments of countries impose systems that allow them to distribute a limited amount of resources evenly among the overall population of their country.
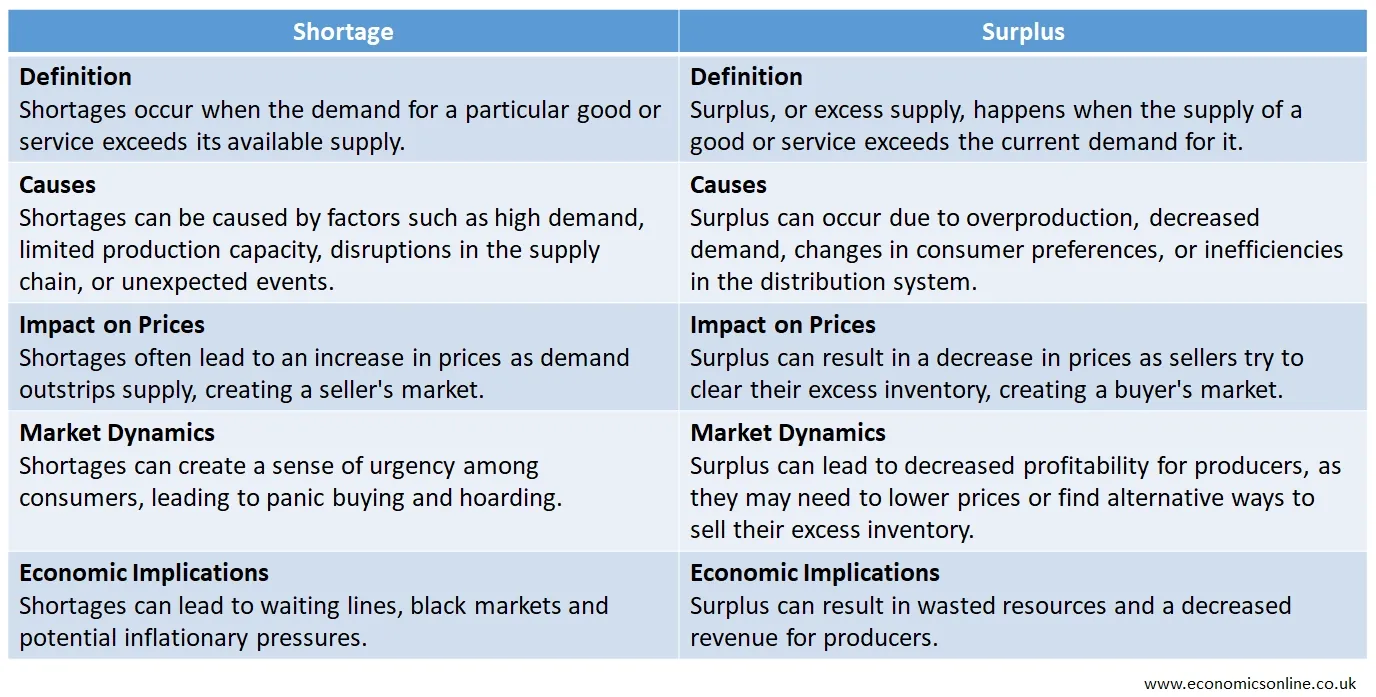
Market Shortage vs. Market Surplus
The following table compares market shortage with market surplus.
Conclusion
In conclusion, shortages occur due to the demand for products in excess to their supply. A country facing different types of shortages, like food shortages, water shortages, energy shortages, etc., cannot work effectively on innovation and infrastructure. Shortages must be addressed correctly so that the markets work effectively for better resource allocation.


