An image of a cyberbrain.
AI Increasingly Powers Economic Shifts in the Market
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence, or AI, refers to the display of human-like intelligence and problem-solving capabilities by computers and machines. It is a branch of computer science that is involved in the manufacturing of smart machines and systems that are capable of performing tasks traditionally associated with or dependent on human intelligence. Artificial intelligence uses many approaches to make tasks easier to perform, such as machine learning or deep learning systems. In the past, the inventions of the printing press, the steam engine, and electricity revolutionised the global economy. Now, AI is creating a digital revolution by affecting every sector of the industry and economy. Artificial intelligence surrounds everything, including creative tools like an AI image generator that push the boundaries of digital innovation.
AI Technologies
The following are some major types of AI technologies that fall into the context of the digital economy:
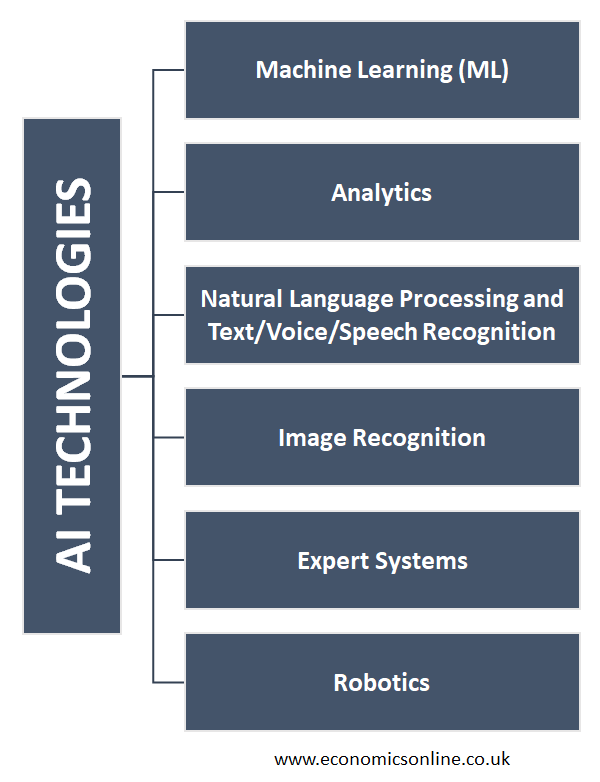
Machine Learning (ML)
A group of AI technologies based on the purpose that machines can be enabled to learn from data and algorithms is known as machine learning. These ML technologies automatically make analytical models to make decisions with no human interaction. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) and deep learning are two major AI technologies that fall under the umbrella of machine learning (ML).
Analytics
This also falls under the umbrella of machine learning (ML) but is also important on its own. AI analytics has the ability to analyse the huge amount of data available in many areas of the digital economy through its computational power and give smart, accurate, and predictive insights, for strategic planning and decision making in the digital economy. Additionally, task mining is emerging as a crucial tool within AI analytics, enhancing process intelligence through desktop analytics.
Natural Language Processing and Text/Voice/Speech Recognition
Natural Language Processing, or NLP, refers to the branch of AI which is involved in enabling computer systems to understand and generate human-like responses. Text and voice recognition systems are used to identify written and spoken works, and then natural language processing systems are used to understand the meaning of context. These technologies are very important in the digital economy as businesses are now adopting computer/AI-drive customer-facing interfaces, like self-check-in kiosks at airports and self-ordering kiosks at food restaurants.
Image Recognition
Computer vision, or image recognition, is the ability of a computer to see images of objects and recognise them. This AI technology is very important for AI systems implemented in robots, such as industrial robots, semi-autonomous or autonomous vehicles, or in vision-impaired humans.
Expert Systems
These systems use subject-specific databases to process the judgement of subject-matter experts and solve complex problems while exhibiting human like intelligence.
Robotics
This is the intersection of multiple technologies, such as engineering and AI. 90% of all robots assembled cars in 2005. In 2019, this was reduced to 50%, but robots are now replacing humans in almost all industries, causing job losses.
Key Sectors of the Digital Economy
The following are some key sectors of the digital economy:
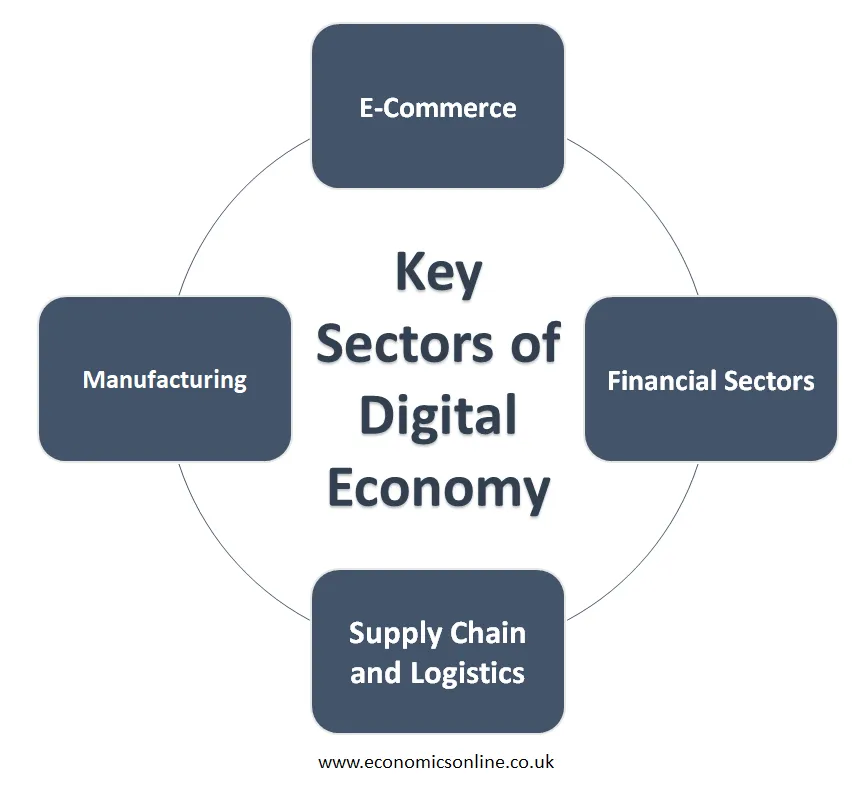
E-Commerce
E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services with the help of the internet. This means that buyers and sellers can participate in trade irrespective of their geographical location. Due to AI, marketplaces are expanding, not only in regions but worldwide through the internet. With the help of AI, anyone can operate an online store easily. Business firms are using AI tools such as chatbots that provide product recommendations, visual searching, and voice recognition to help customers improve their shopping experience.
Financial Sectors
Banks and other financial institutes are also using AI and ML tools to streamline their internal activities and provide better services to customers. Banks are providing access to AI-driven tools to their customers in order to monitor budgets, make suggestions in spending decisions, and provide personalised, computer-generated financial advice. With the help of AI, banks provide customer with a platform for their self-help round the clock. Additionally, customers also have the option of using robot trading AI system to make their trades.
Supply Chain and Logistics
The supply chain and logistics are revolutionised by the digital economy and e-commerce. The complexity of the supply chain and logistics increases due to increase in sales volumes in the digital economy. In the traditional economy, businesses are limited by their ability to deliver products and services in their stores. But now businesses are shifting towards the digital economy and taking advantage of AI and AI technologies in supply chain and logistics to become effective partners between suppliers and customers in global markets in order to meet their expectations.
Manufacturing
The use of AI in the manufacturing of goods and the automation of machines has been in the industry for quite some time. With the help of robots, manufacturing and recurring processes become easier, less tiring, and more cost-effective, as no human is directly involved in the manufacturing process. Intelligent robots individually monitor the quality of manufactured products and automatically detect defective products, minimising the probability of future defects. Robots and AI are both used in all types of manufacturing processes.
Effects of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on Jobs and the Economy
According to the McKinsey Global Institute, artificial intelligence has a significant impact in terms of creating additional global economic activity of about $13 trillion in the coming years and, by 2030, about 16% higher cumulative global GDP as compared to now. This will lead to the creation of about 1.2% additional economic growth per year. This will also lead to the substitution of labour by robots and automated machines to make products faster and at a lower cost. According to Forbes, AI has the potential to be one of the most disruptive technologies in global economies.
Will AI Cause Unemployment?
According to Goldman Sachs, AI will replace 300 million full-time jobs throughout the world by 2030. It can also replace 25% of jobs in Europe and the U.S., which means an increase in unemployment in the labour markets of these geographical regions. According to another report, 66% of the jobs in the U.S. and Europe are at the risk of being replaced by AI.
According to an MIT and Boston University report, Forbes says that AI use will replace two million manufacturing workers by 2050.
According to a report by the McKinsey Global Institute, by 2030, approximately 14% of workers globally will need to shift their careers due to digitalisation, automation, AI advancements, and robotics.
According to the World Economic Forum, by 2050, 85 million jobs will be replaced by AI. Moreover, AI is forecasted to replace two-third of the jobs in the retail industry by 2050. This will happen due to technological advancements in terms of e-commerce, and rising labour costs for retail businesses.
However, AI is creating many new jobs which may result in a fall in unemployment. These jobs may require new skills related to computer science and AI.
Jobs that will Probably be Computerised
The following are some jobs that will probably be computerised and automated:
- Customer Service Representative
- Receptionists
- Accountants
- Salesperson
- Research and Analysis
- Warehouse Work
- Insurance Underwriting
- Retail
Jobs that Probably will not be Computerised
The following are some jobs that will not probably computerised and automatic:
- Teachers
- Judges
- Directors
- Managers
- CEOs
- HR Managers
- Psychologists and Psychiatrists
- Surgeons
- Computer System Analysts
- Artists and Writers
Effects of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on Society and the Future
According to Forbes, AI has many possibilities and applications that simplify our lives to a great extent. It will shape the future and fate of humanity.
According to Bernard Marr & Co., the transformative impact of AI on our society will have extensive legal, economic, regulatory, and political implications for all types of jobs, including industries we are preparing for.
Furthermore, AI is bringing some positive changes in the lives of people in terms of better access to education and improved healthcare. For example, AI chatbots such as ChatGPT or Gemini are helping students in their studies. This will lead to a higher standard of living of people.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Business Firms
The following are some of the major advantages of artificial intelligence for businesses:
Improved Customer Experience
The solutions generated by artificial intelligence help businesses quickly respond to the queries and questions of their customers and address them in an efficient way. Chatbots are now linked with conversational artificial intelligence through natural language processing which generates personalised messages to find the ideal solution for their needs. This may lead to an improvement in terms of customer experience.
Effective Decision-Making
Artificial intelligence correlates with data delivery, generates data consistency, analyses market trends, improves uncertainties, and also provides estimates and forecasts for better and more effective decision-making process.
Automation
With the help of automation, businesses can benefit from a boost in productivity and high production rates in sectors such as communication, transportation, customer products, and service industries. Automation supports freeing resources that can be used in other processes.
Research and Data Analysis
Artificial intelligence combined with machine learning (ML), which enhances the process of data analysis by predicting algorithms and models to process and gauge data for relevant trends, also speeds up the process of analysing and processing data for research and development purposes.
Solutions of Complex Problems
The advancement of artificial intelligence technologies from basic machine learning (ML) to deep learning (DL) helped businesses find accurate solutions for complex problems, resulting in better efficiency in solving issues, which means improved productivity and reduced expenses.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Industries
With the help of artificial intelligence, different sectors and industries can organise their operations and become more efficient. The following industries and sectors are transformed by artificial intelligence:
Education
With the help of AI, the education sector developed many techniques and learning programmes along with gaming and software programmes that were used to reform and redesign the whole education system and provide help to those students who have special needs.
Business Intelligence
Business intelligence is the technology that introduced the concept of prediction and is used to make effective decisions through the use of AI tools and apps. Business intelligence also uses data effectively to improve results.
Manufacturing
With the help of AI, manufacturing units can benefit from automation, decision-making, integration, and channeling effortlessly. It is predicted that the production process will be enhanced by 40% by 2035 with the use of AI.
Agriculture
AI and autonomous farming are used to predict consumer demand and supply chain behaviour at the regional level and are also used to predict weather conditions that affect the harvesting process.
Cybersecurity
With the help of AI, we can find the hackers before the attack launches. AI has improved itself and is used to learn threats in the current business environment. Experts are using AI to reduce the number of threats and hacks.
E-Commerce
Businesses implement machine learning systems to build strong customer relationships; for example, Amazon is a powerful AI platform that uses AI in each and every step of a customer’s life cycle.
Impact of AI on the Global Economy
AI is a global phenomenon, and may have a huge impact on the global economy. According to a study by PwC Global Artificial Intelligence, AI will contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy, by 2030, directly or indirectly. Almost half of this total economic gain will come directly from product improvements and increased consumer demand. Because AI will generate good product variety using increased personalisation, affordability, and attractiveness over time. This contribution from AI will be beneficial for all regions. The greatest economic gain from artificial intelligence will be in China, which will see a 26% increase in GDP, and in North America, which will see a 14.5% increase, by 2030.
Conclusion
In conclusion, artificial intelligence is beneficial for both the traditional and digital economies of the world. AI and its related technologies are being adopted by business firms and industries around the world. This is causing a major shift towards a digital economy. However, AI is negatively affecting the workforce and the labour market as robots take over the positions of humans. Due to this shift, work is done more accurately and timely, but unemployment may increase globally.