
Photo by Artem Beliaikin / Unsplash
Penetration Pricing
What is Penetration Pricing?
Penetration pricing means setting the price of a new product or service initially very low and then gradually increasing it over time. This low price is often supported by strong promotion in order to achieve a high volume of sales and capture a large market share. If the product gains a large market share, then the price can slowly be increased. This pricing is also called market penetration pricing.
Why is Penetration Pricing Used?
Pricing is a crucial aspect of any business strategy. The primary objective of penetration pricing is to capture market share by offering a lower price than competitors. This lower price point will generate demand and build a customer base in a short time. The theory behind this strategy is that a low initial price will disrupt existing businesses by luring customers away with a much lower price. By attracting customers with a lower price, businesses can establish themselves in the market and gain a foothold. Once they have captured their targeted market share, they can raise prices to increase profits and reflect the product's rising value.
Understanding the Working of Penetration Pricing
The market for a product can be divided into different layers of customers based on their purchasing power. The customers with low purchasing power make up the highest proportion of the market. In penetration pricing, a business enters the market from its lower end by setting an initial low price, as shown in the following diagram.
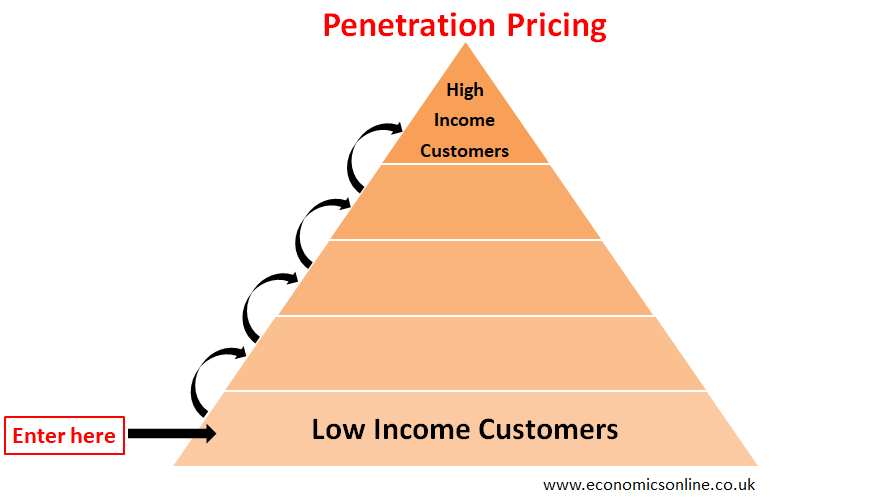
This low price serves as a powerful incentive for customers to choose the new product over existing alternatives. As a result, the business can rapidly gain a substantial portion of the market. Once the lowest layer is captured and the market share is established, the price can then be increased gradually to target other layers of the market as well.
Conditions for using Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is considered a suitable and appropriate pricing strategy if the following conditions are met.
- The business is using mass marketing, and the objective is to get a large market share.
- There is a little product differentiation in the market. The product offered by the business is not so unique or truly innovative. For high-quality and innovative products, price skimming may not work.
- The business is aiming to get economies of scale benefits, which are only possible when production is done on a large scale.
- The demand for the product is price-elastic (PED > 1). It means the customers should be price sensitive, and charging a lower price should increase the quantity demanded by a large percentage.
What Types of Products are Suitable for Penetration Pricing?
Penetration pricing is suitable for those products that are used by mass markets and are not so unique and innovative. Some examples of such products include the internet, cable, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) products.
The Users of Penetration Pricing
There are two primary users of penetration pricing, as explained below:
New Businesses
Penetration theory is often used by businesses that are new to the market. These firms use penetration pricing to steal market share from existing firms.
Established Businesses that Offer New Products
Established firms can also use penetration pricing when they launch new products. Since these companies may have enough resources available, they may be able to sacrifice short-term profits to establish their new products.
Real-world Examples of Penetration Pricing
Netflix
Netflix is a prime example of successful penetration pricing. When Netflix expanded its streaming services globally, it adopted penetration pricing by offering low monthly subscription fees. This strategy helped Netflix quickly establish itself as a dominant player in the streaming industry.
Amazon
Amazon used penetration pricing when it first launched its Kindle e-reader by offering it at a lower price. This strategy worked, and Kindle became a huge success.
Uber
Uber is another example of successful penetration pricing. Uber used penetration pricing when it first entered the market by offering lower prices than traditional taxis.
Digital Content
Publishers and authors often release e-books, magazines, and digital content at lower prices initially to attract readers and build a following. Once a fan base is established, prices might be adjusted to reflect the perceived value of the content.
Advantages of Penetration Pricing
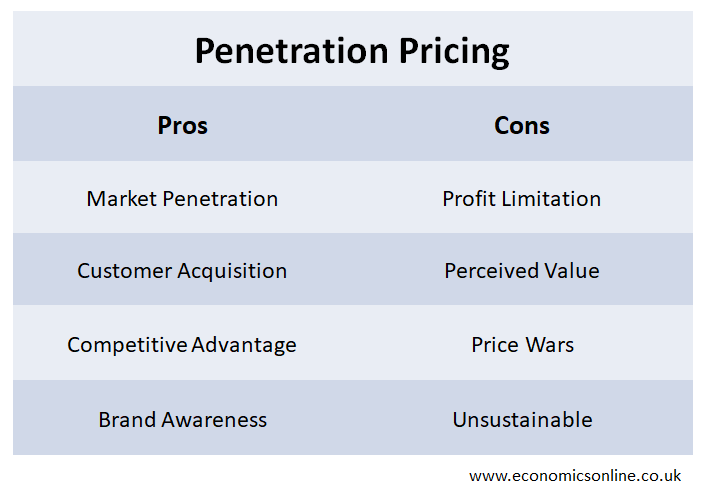
Market Penetration
Penetration pricing is highly effective at quickly penetrating the market. The low price point entices price-sensitive customers to try the new product and this helps the firms to establish a strong foothold in the market.
Customer Acquisition
Penetration pricing helps firms attract a large number of new customers who might have been hesitant to try the product at a higher price. This helps the firms to build a good customer base.
Competitive Advantage
Selling the product at a lower price can be a source of competitive advantage, making it difficult for competitors to match or beat the price without affecting their profitability.
Brand Awareness
Penetration pricing is often accompanies by a strong promotion which can generate buzz and curiosity about the new product, leading to increased brand awareness.
Disadvantages of Penetration Pricing
Profit Limitation
One of the main drawbacks of penetration pricing is that it initially sacrifices profit margins. Companies might not see substantial profits until they realise economies of scale or raise prices after gaining a significant market share.
Perceived Value
A low price might lead some customers to perceive the product as low quality. This can impact the brand's image and positioning in the long run.
Price Wars
If one firm will start using penetration pricing, then its competitors may respond by lowering the prices of their products as well, sparking a price war that could erode profitability for all firms.
Unsustainable
Maintaining a low price in the long term might not be sustainable, especially if production costs or market conditions change.
Penetration Pricing Strategy: Is It Right for You?
Penetration pricing can be a powerful tool for firms aiming to swiftly gain market share and establish a strong customer base. However, it requires careful consideration of the right conditions, which are mentioned above, and potential trade-offs, including short-term profit limitations and potential brand perception challenges.
Conducting thorough market research and understanding your target audience's sensitivity to price changes is essential before implementing this market penetration strategy. Moreover, there should be a little product differentiation in the market.
Tips for Successful Penetration Pricing
The following tips might be helpful for those firms that are planning to use penetration pricing strategy.
Build Long-term Loyalty
Using penetration pricing to gain market share quickly is a short term approach. In the long-term, firms should focus on building customer loyalty in order to create brand recognition and loyal customer base.
Increase the Price Slowly
After setting the initial price at a low level, firms should increase the price of their products to make them more profitable. This should be done slowly after making customers loyal, otherwise, customers can respond negatively and go to other firms to purchase substitutes.
Improve the Product
The initial success of penetration pricing will give a customer base to the business. These customers should be kept and taken care off. One way is by gradually improving the product. This product improvement will create brand loyalty and will also justify the gradual price increase.
Penetrating Pricing vs. Market Skimming
Penetration pricing and price skimming are the two pricing strategies used by firms for new products in the introduction stages of their life cycles. Some points of difference between penetration pricing and price skimming are given below:
Definition
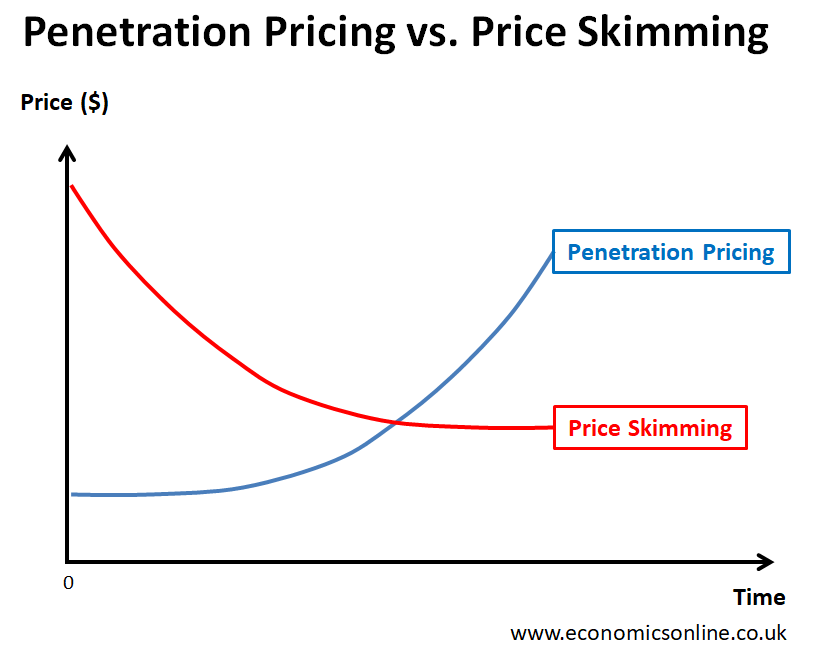
While penetration pricing involves setting a low introductory price of a new product and then gradually increasing the price over time, price skimming means setting the initial high price for a unique or innovative new product and then gradually decreasing the price over time.
Objective
While the objective of penetration pricing is to gain a significant market share quickly, price skimming strategy is aimed at recovering the research and development costs of the product quickly before the entry of competitors. When competitors enter, the price is gradually decreased to keep them away.
Target Customers
Penetration pricing is used to target customers with low purchasing power, while price skimming is used to target high-income customers who are early adopters and who are willing to pay the premium price.
Conditions
Penetration pricing is used in cases of price-elastic demand, while price skimming is used in cases of price-inelastic demand. Moreover, economies of scale, is not the objective of firms, at least in the short run, when using price skimming.
Conclusion
The price penetration strategy involves setting the initial price of a new product as low as possible to quickly capture a reasonable market share. This pricing technique can be very effective for businesses looking to enter a new market or disrupt existing businesses. However, penetration pricing requires significant resources in terms of production, marketing, and distribution of the products. Before implementing this pricing strategy, businesses should consider their marketing and pricing objectives, the conditions of penetration pricing, and its pros and cons. They should also analyse if they have enough resources to use and sustain penetration pricing effectively.


