An image of the US flag and dollar bills.
Capital Account of the Balance of Payments
Introduction
A capital account is a component of the balance of payments that contains the record of the acquisition and disposal of non-produced and non-financial assets along with capital transfers. In order to better understand the capital account, let us explore the balance of payments and its components.
Balance of Payments (BOP)
A systematic and comprehensive record of a country’s financial transactions (including imports, exports, and financial flows) with the rest of the world in one year is called the balance of payments of that country.
Imports
Those goods and services that a country buys from other countries are called imports. Visible imports are the imports of goods such as machinery, food items, and raw materials for manufacturing purposes. Invisible imports are the imports of services, such as educational services. Imports generate an outflow of money.
Exports
Those goods and services that a country sells to other countries are called exports. Visible exports are the exports of goods such as cars, electrical appliances, and agricultural goods such as seeds and fertilisers. Invisible exports are the exports of services, such as IT services. Exports generate revenue for a country and are considered an inflow of money.
Financial Flows
The movement of money between different countries is called financial flow. These can be remittances, loans, investments in foreign assets or currencies, etc.
Components of the Balance of Payments
The following are four components of the balance of payments:
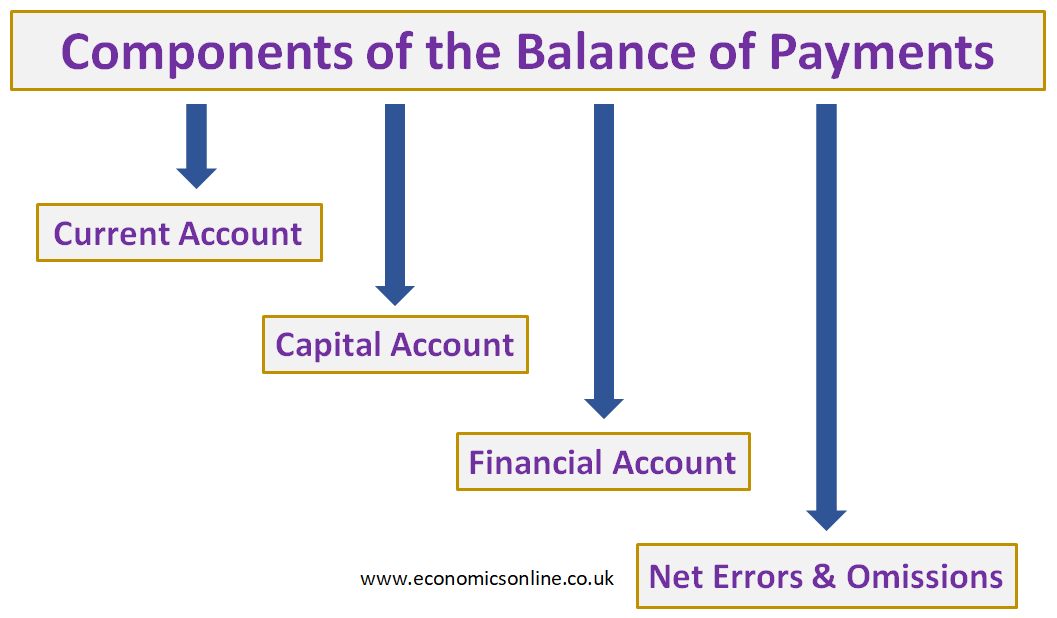
The Current Account
This is the first component of the balance of payments. It consists of the following four parts:.
Trade in Goods
Trade in goods includes visible exports and visible imports.
Trade in Services
Trade in goods includes invisible exports and invisible imports.
Primary Income Account
This includes the inflows and outflows of money in the form of rent, wages, interest, and profits.
Secondary Income Account
This includes the inflows and outflows of money in the form of remittances, gifts, donations, etc. These are also called current transfers.
The current account balance is calculated by using the following formula:
Current Account Balance = Goods Balance + Services Balance + Primary Income Balance + Secondary Income Balance

The Capital Account
The capital account in balance of payments is an account that is used to record the acquisition and disposal of non-produced and non-financial assets along with capital transfers. This includes the sale or purchase of real estate, patents, trademarks, licences, leases, marketing assets, or copyrights.
The Financial Account
This account is used to record inflows and outflows of financial assets and liabilities. These include foreign direct investments, portfolio investments, the flow of foreign currencies, and gold.
The Balance of Payments Formula
The following is the formula for the balance of payments.
Current Account Balance = Capital Account Balance + Financial Account Balance

Net Errors and Omissions
Net errors and omissions is a balancing item that is used to assure the arithmetical equality of debit and credit when errors occur in the compilation of statistics regarding the current, capital, and financial accounts.
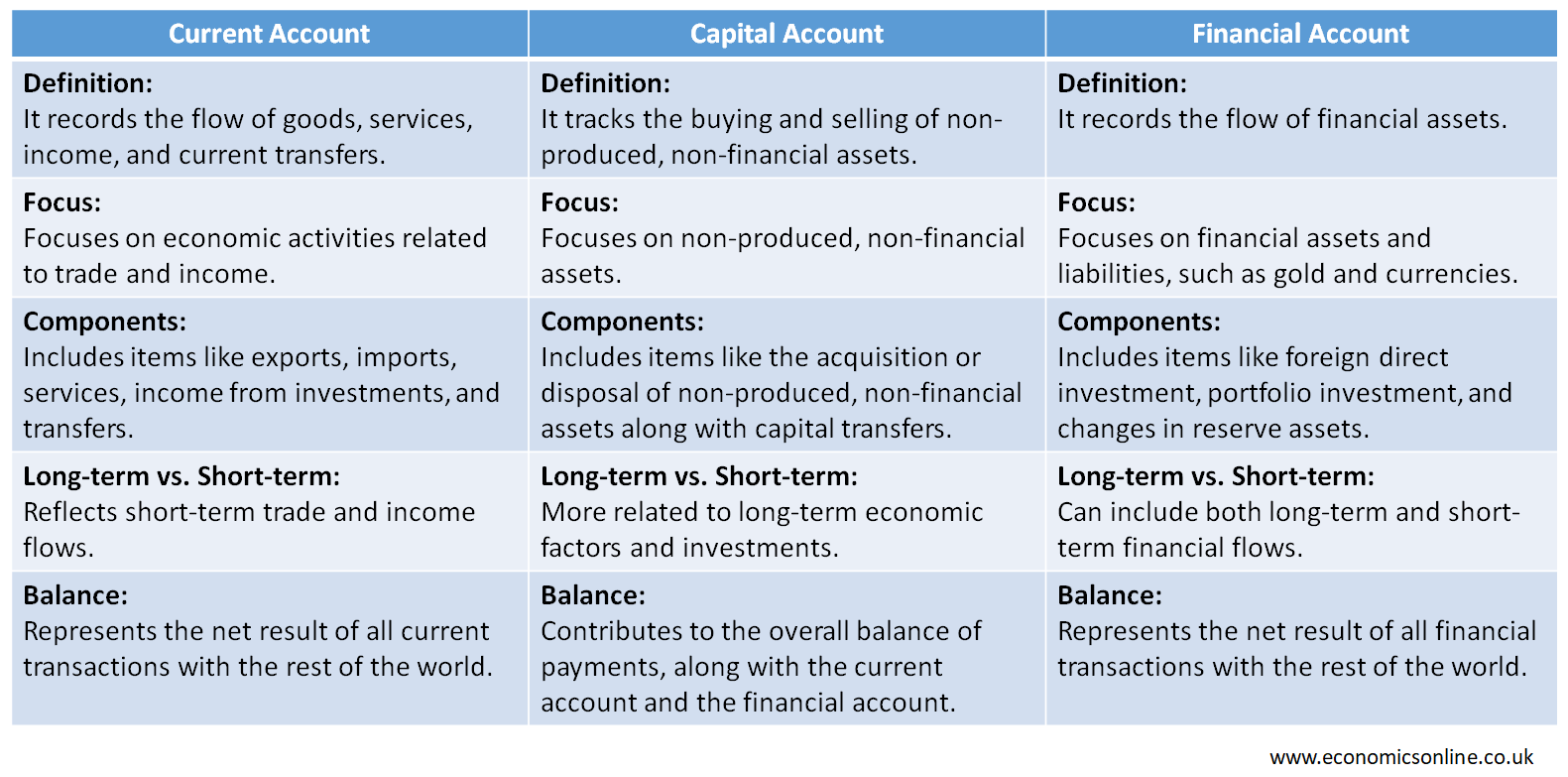
Current Account, Capital Account and Financial Account
The following table compares the main features of the current account, capital account, and financial account.
Importance of Current Account
The following two points explain the importance of the current account of balance of payments:
Balance of Trade (BOT)
The difference between the value of exports and the value of imports is called the balance of trade (BOT), or trade balance.
Balance of Trade (BOT) = Value of Exports – Value of Imports

The balance of trade is also called net exports and is an important component of the aggregate demand of a country. A balance of trade surplus can increase aggregate demand and boost growth and employment in the country.
The current account contains the trade balance of a country with the rest of the world by keeping record of the import and export of goods or services from that country to others. This also shows us how competitive a country is in contrast to others.
Foreign Exchange Reserves
A large amount of foreign exchange reserves represents a heavy current account balance for that specific country. When economic crises happen, these reserves hold the backbone of a country’s economy and keep its exchange rate stable.
Importance of a Capital Account
The following two points explain the importance of the capital account of the balance of payments:
Economic Development
A capital account helps to enhance the economic development of a country as it engages other countries in investing in non-financial assets, investments in infrastructure such as building motorways that connect countries, and some sort of technology as well.
Wealth Accumulation
A capital account also helps in wealth accumulation by acquiring precious non-financial assets such as copyrights, patents, land, and other natural resources.
Importance of Financial Account
The financial account is helpful in keeping the record of foreign investments, such as foreign direct investment and portfolio investment. In this way, countries can earn external capital and enhance their economic conditions.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
The investment of money made by an individual, a company, or a corporation of one country into another country is known as foreign direct investment (FDI). In foreign direct investment, the purpose of investing in foreign countries is to establish business setups and acquire the desired amount of assets from foreign countries.
Foreign direct investment is beneficial for both the investing and recipient countries. It provides opportunities for higher ROI, access to new resources, and market expansion for investing countries. It also creates job opportunities, technology transfer, greater production capacity, and high economic growth for the recipient country.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the capital account of the balance of payments is an account that is used to record the transfer of non-produced and non-financial assets between different countries. The trade of non-financial assets includes the sale or purchase of real estate, patents, or copyrights between countries on legal terms. The capital account helps a country with wealth accumulation and economic development.


