An image of a women enjoying sunset on a beach.
Human Development Index (HDI)
Introduction
The level of happiness or well-being the citizens of a country are enjoying is called its standard of living. It is the quality of life of people of a country. Economists use different methods to measure the standard of living of people of a country. These methods include per capita income, Net Economic Welfare (NEW), Measurable Economic Welfare (MEW), Human Development Index (HDI), Multi-dimensional Poverty Index (MPI) and many more. In this article, we will discuss Human Development Index (HDI) in detail.
What is Human Development Index?
Human Development Index is a statistical tool developed by the United Nations to measure the economic and social well-being of the people of a country by considering their health, education and standard of living. Human Development Index is abbreviated as HDI. It is also called human growth index, which is used to gauge and compare the level of human development within and between countries. HDI is a composite measure which considers three indicators of economic development (health, education and income).
Historical Background
In 1990, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) developed the human development index. This was a time when only GDP and other national income statistics were used to assess the economic growth and development of a country. HDI was developed to give importance to the other dimensions of development of a country, such as education and health, not just economic growth.
Understanding Human Development Index
HDI is a composite measure of economic development. Let’s begin by understanding the difference between economic growth and economic development.
Economic growth refers to an increase in the real GDP (national output or national income) of a country over a period of time. It is measured by an increase in the per capita income of the people of a country. For example, if GNI per capita is increasing, we will say that there is economic growth in the country.
Economic development refers to an increase in the standard of living of the people of a country over a period of time. Economic growth does not mean an increase in the standard of living of the people of a country. In fact, economic development is a broader concept than economic growth.

A country may be producing more output (say, weapons), but the standard of living of the people may be low due to a low literacy rate and poor health. This is where HDI will play its role as a composite measure, which includes health and education dimensions as well as per capita income.
Dimensions and Indicators of HDI
The three dimensions and four indicators of HDI are illustrated in the diagram below: These are given a weight of one-third each.
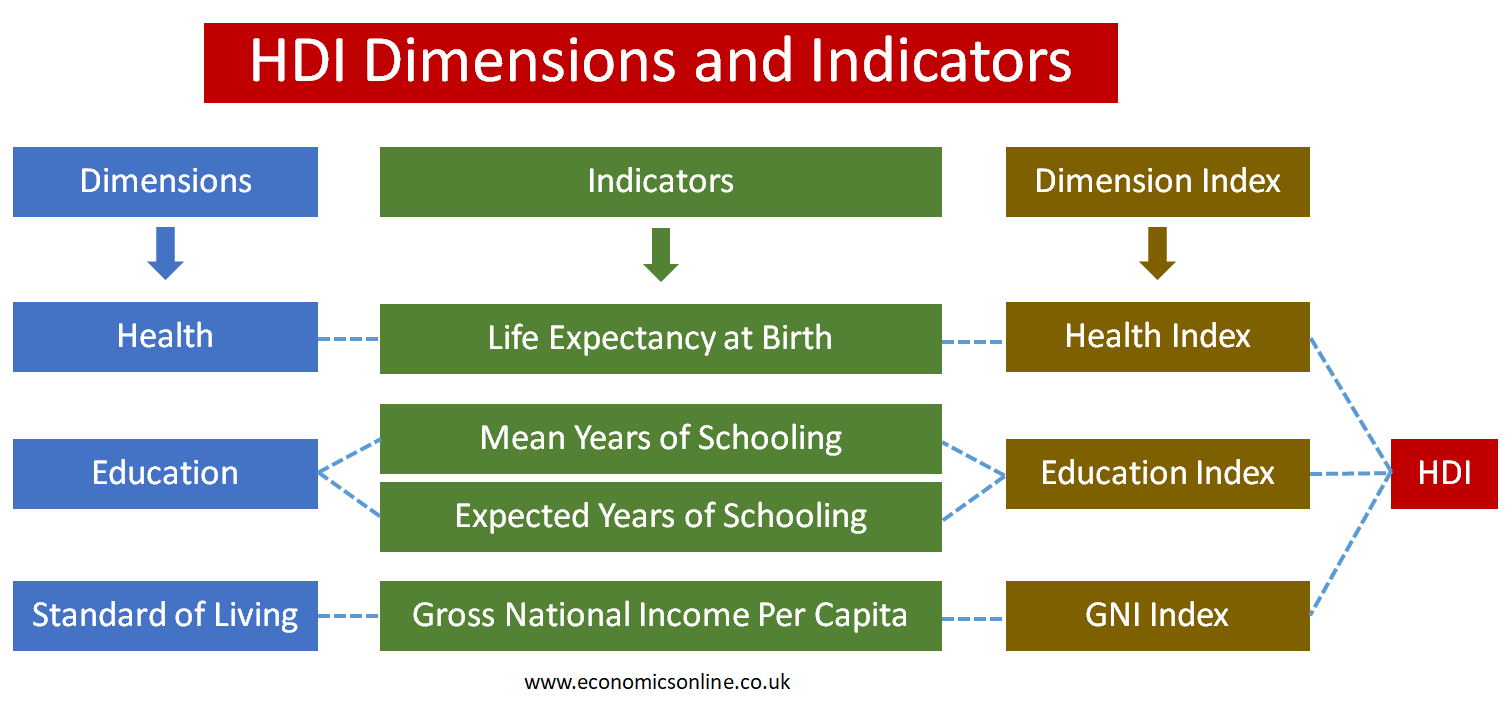
The Health Dimension
The health dimension in HDI, means living a long and healthy life. It is indicated and measured by life expectancy at birth. Life expectancy means the expected life of an individual to live in a specific country. Life expectancy is an important part of HDI that explains the expected life of an individual from birth until death that he is going to spend as a part of the population of that country. This dimension measures the health and quality of life of a country’s population. Based on this, the health index (life expectancy at birth index) is calculated, which accounts for one-third in the calculation of HDI.
The Education Dimension
The education dimension in HDI means the level of knowledge people acquire in a country. This has two indicators: mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling. The mean year of schooling is used to measure the average number of years of education gained by adults of age 25 and above. And the expected year of schooling is used to measure the expected number of years of schooling a child is going to receive. Based on this, the education index is calculated, which accounts for one-third in the calculation of HDI. It is important to note that before 2011, the adult literacy rate was used instead of mean years of schooling in the calculation of HDI.
The Standard of Living Dimension
The standard of living dimension in HDI means, enjoying a decent standard of living and quality of life in a country. The standard of living is measured by using the gross national income per capita (GNI per capita). GNI per capita means the average income of an individual living in a county. Based on this, the GNI index is calculated, which accounts for one-third in the calculation of HDI.
HDI Values
The HDI value of a country can be from 0 to 1. The HDI values vary between countries based on their HDI dimensions or indicators. Every year, the United Nations publishes HDI value of 193 countries along with their HDI rankings. There are four levels of HDI values, which are given below:
1. Low Human Development (HDI is less than 0.550)
2. Medium Human Development (HDI is from 0.550 to 0.699)
3. High Human Development (HDI is from 0.700 to 0.799)
4. Very High Human Development (HDI is 0.800 or more)
Countries can determine their level of human development by looking at their HDI values.
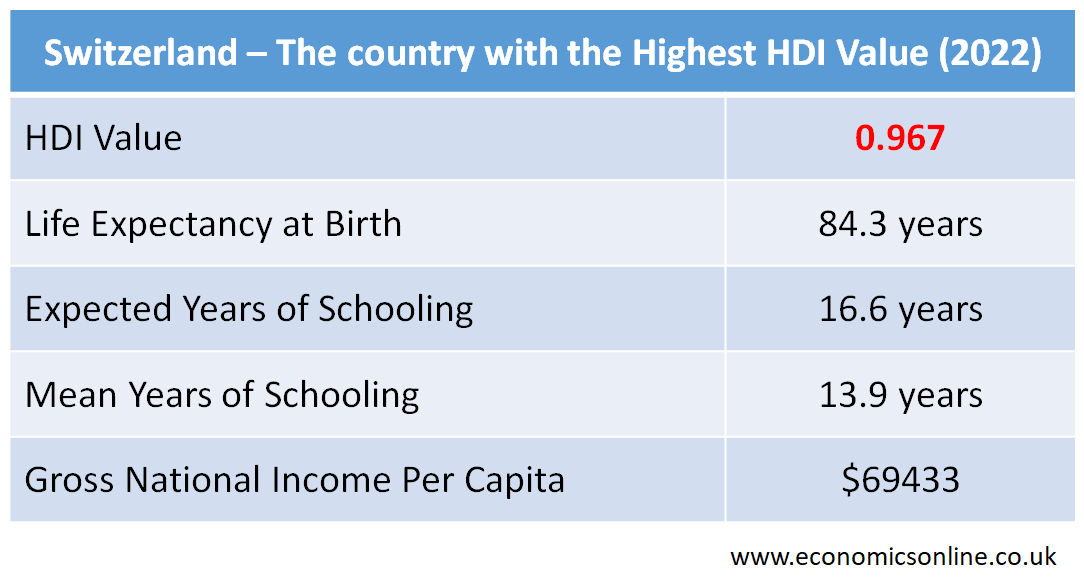
Country with the Highest HDI Value
In 2022, Switzerland scored the highest value of HDI, which was 0.967, with an improvement of 0.002 as compared to 2021. It is ranked at number 1 among 193 countries in terms of human development. It is a country with a high level of human development. GNI per capita is in PPP (purchasing power parity).
Other Countries with high HDI
The following are some other countries that have a high value of HDI:
Norway
Norway is ranked at number 2 among 193 countries after Switzerland and it has the value of HDI equal to 0.966 (2022), just 0.001 less than that of Switzerland. It is also a country with very high level of human development. Norway has a high HDI value because it has a better education system, a high life expectancy, and a stable economy compared to other countries on the list.
Iceland
Iceland is ranked at number 3 among 193 countries after Switzerland and Norway and it has the value of HDI equal to 0.959 (2022). It is also a country with very high level of human development. Iceland also has a high value of HDI because this country also provides a high quality of life to its citizens.
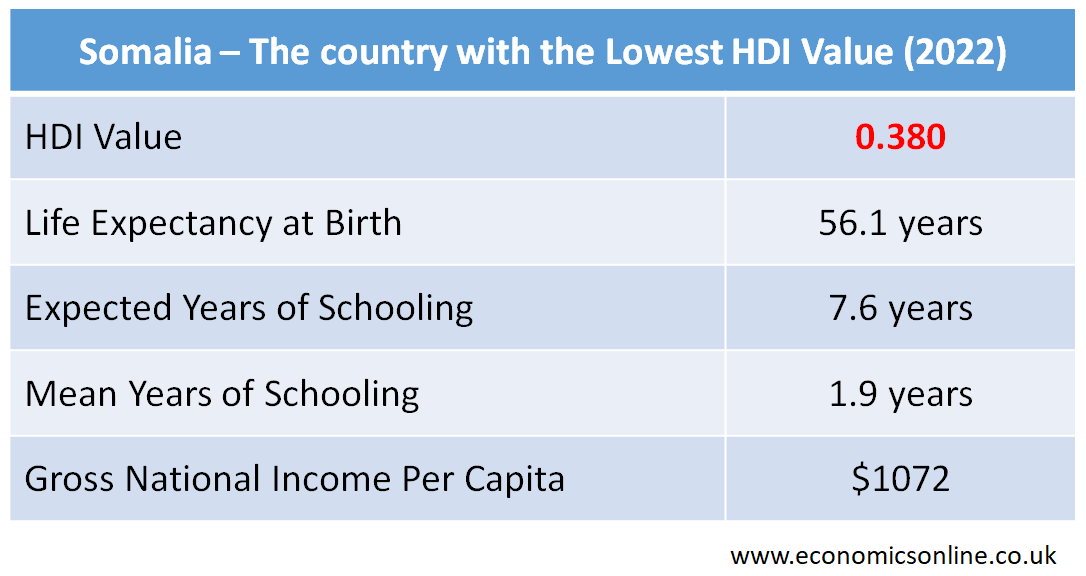
Country with the Lowest HDI Value
In 2022, Somalia scored the lowest value of HDI, which was 0.380. It is ranked at number 193 among 193 countries in terms of human development. It is a country with the lowest level of human development.
Other Countries with low HDI
The following are some other countries that have a low value of HDI:
South Sudan
South Sudan is ranked at number 192 among 193 countries and it has the value of HDI equal to 0.381 (2022), just 0.001 more than that of Somalia. It is also a country with low level of human development. South Sudan has a low HDI value because it is the youngest country in the world and gained independence from Sudan in 2011. South Sudan is facing serious economic problems, high poverty rates, and limited availability of basic resources.
Central African Republic
The Central African Republic is ranked at number 191 among 193 countries and it has the value of HDI equal to 0.387 (2022). It is also a country with low level of human development. The Central African Republic has low HDI value because this country faces serious political instability, due to which individuals are unable to access the basic necessities of life such as basic needs of food, clothing and shelter.
Types of Human Development Index
The following are some of the main types of HDI:
Standard HDI
As the name says, it is a standard index that assesses and compares the three dimensions of HDI and also provides the overall health and development levels of different countries.
Inequality-Adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI)
This type of HDI is used to analyse the inequalities in education, health, and per capita income within a country. This index is used to identify inequalities and provide a clear understanding of the development levels of different countries.
Gender Development Index (GDI)
This type of human development index is used to identify gender inequalities within a country. This index is used to explain gender disparity such as female education, women’s life duration, and female per capita income. This index provides information about the impartiality and development levels between males and females in different countries.
Importance of HDI
The following points explain the importance of HDI:
Measuring Economic Development
HDI is used to measure the economic development of a country. It provides a clear understanding of a country’s well-being, including the expected life expectancy at birth, education, and income per capita of every individual. For example, HDI indicates that a mere increase in national income may not indicate economic development. For example, a higher production of military equipment and weapons may increase national income and will be reflected in higher value of GNI per capita, however, people may have a low quality of life.
International Comparisons
HDI is also used to compare different countries on the basis of development levels. This index is also used to identify inequalities between countries and those areas that need improvement.
Policy Planning and Targeting
HDI is also used by governments to evaluate their performance from time to time. With the help of the human development index, governments are able to make their national policy choices and set their government policy priorities, for example, the allocation of resources, improvements in the health and education sectors, etc.
Advocacy and Accountability
HDI is also used to enlighten the development issues in different countries. This index makes the government accountable for their deeds. This index is used to evaluate the progress, economic health, or well-being of a country during a specific government.
Limitations of HDI
The following are some limitations of HDI:
Simplified Measurement
The human development index oversimplifies the diverse nature of economic development. This index ignores the inequalities of some factors between different countries that are important for a country’s well-being. For example, it does not account for human security and safety, women empowerment, poverty and income inequality.
Data Limitations
The human development index is dependent on accessibility and quality. This index does not provide accurate data in some situations because the data it uses may be limited, incomplete, or outdated, due to which we are unable to understand the complete picture of economic development levels.
Lack of Contextual Information
The human development index does not provide information about the inequalities and serious economic challenges in different countries. It lacks information about local or regional differences, due to which this index is unable to explain the localised development problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HDI is the most popular summary measure of human development. It is used to compare the development levels within and between countries. This human development index is used by governments to evaluate their own progress within a particular time period. The human development index value explains the health of a country’s well-being. However, HDI also has limitations, such as a lack of contextual information and oversimplification.


