
An image of dollar bills and a text costs.
Implicit vs. Explicit Costs
Introduction
In the subjects of economics, accounting, and business studies, the concept of cost is critical in understanding cost control, efficiency, profit calculation, breakeven analysis, optimisation, and many other topics. There are different types of costs, and in my student life, I remained confused about the true meaning and use of different types of costs in decision-making. In this article, I will explain the meaning of implicit and explicit costs and their use in decision-making.
What is a Cost?
Cost refers to the sacrifice of financial resources in order to get some benefit in the future. There are many types of costs, including fixed costs, variable costs, semi-variable costs, short-run costs, long-run costs, marginal costs, total costs, average costs, direct costs, indirect costs, and many more. In this article, we will focus on explaining the concept and use of implicit and explicit costs.
Implicit Costs
Implicit costs refer to the opportunity costs of using the resources and are considered important while making economic decisions. These costs are not recorded or mentioned in the financial records of the business, like the income statement and balance sheet. However, these costs suggest the best alternatives that are neglected during decision-making. Let’s suppose that you have decided to start own business (own firm) instead of doing a job. In this situation, the job salary may be considered an implicit cost that you could have earned if you decided to do the job instead of starting your business.
Explicit Costs
Explicit costs are the actual expenses that are incurred when producing certain goods or services. Explicit costs are out-of-pocket expenses. Explicit costs are recorded in the books of accounts and are mentioned in financial records like the income statement and balance sheet. Explicit costs are also called accounting costs.
Wages paid to employees, rent expenses, the cost of raw materials, advertising costs, building or land costs, formal salary (annual salary) which the corporate firm pays, depreciation of goods and other assets, cost of purchasing the tangible assets like furniture, utility costs (utility bills) and shipping costs are some examples of explicit costs.
Economic Cost
Economic cost is the sum of explicit cost and implicit cost. In other words, it is the sum of accounting cost and opportunity cost. Economic cost is greater than accounting cost because of the addition of opportunity cost. The formula for calculating economic cost is given below:
Economic Cost = Accounting Cost + Opportunity Cost
Economic Cost = Explicit Cost + Implicit Cost

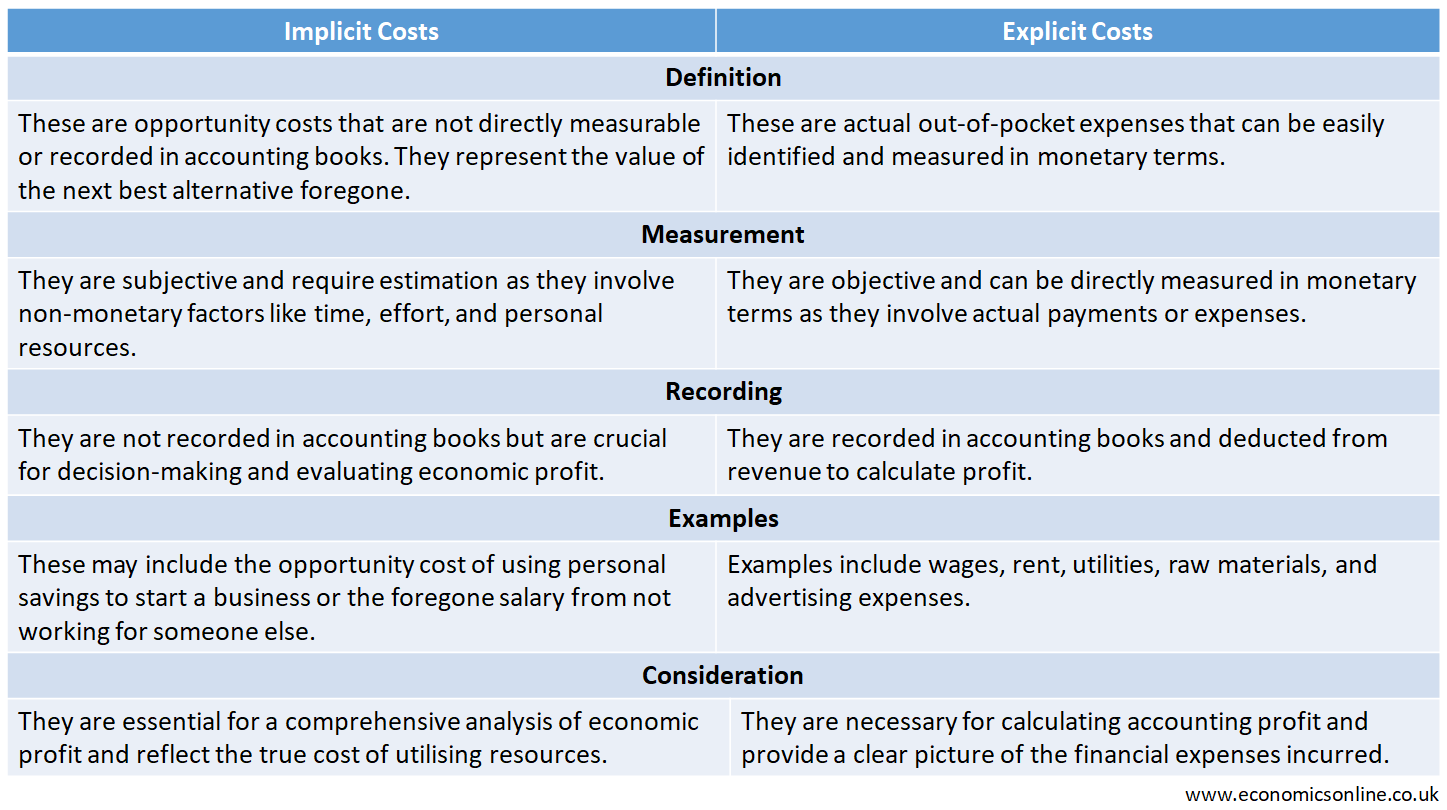
Difference between Implicit Costs and Explicit Costs
The following table summarises the main points of difference between implicit cost and explicit cost.
Total Revenue
Total revenue refers to the total amount of money earned by a business firm by selling goods and services in a given period of time. This is the income earned by selling a firm’s product. Total revenue is equal to the price of the product times the quantity of output sold. The formula for calculating total revenue is given below:

Profit
The difference between total revenue and total cost is called profit. The main objective of almost all the private sector businesses, regardless of their size or complexity, is to increase profit. The formula for calculating total profit is given below:
Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost

Accounting profit and economic profit are the two main types of profit.
Accounting Profit
The difference between the total revenue and total explicit costs (accounting costs) of a business is called the accounting profit. Accounting profit is a profit that can be calculated by using explicit costs mentioned in the income statement. The implicit costs or opportunity costs are not included or considered in the accounting profit. Accounting profit is used to calculate the profitability of a business operating in a market. The formula for calculating accounting profit is given below:
Accounting profit = Total Revenue – Accounting Cost
Accounting profit = Total Revenue – Explicit Cost

Economic Profit
Economic profit is the difference between total revenue and economic cost which is composed of both explicit and implicit costs. The formula for calculating economic profit is given below:
Economic Profit = Total Revenue – Economic Cost
Economic Profit = Total revenue - (Explicit Cost + Implicit Cost)

There are three types of economic profit, which are given below.
If economic profit is positive, it is called abnormal profit or supernormal profit.
If economic profit is zero, it is called normal profit.
If economic profit is negative, it is called subnormal profit or loss.
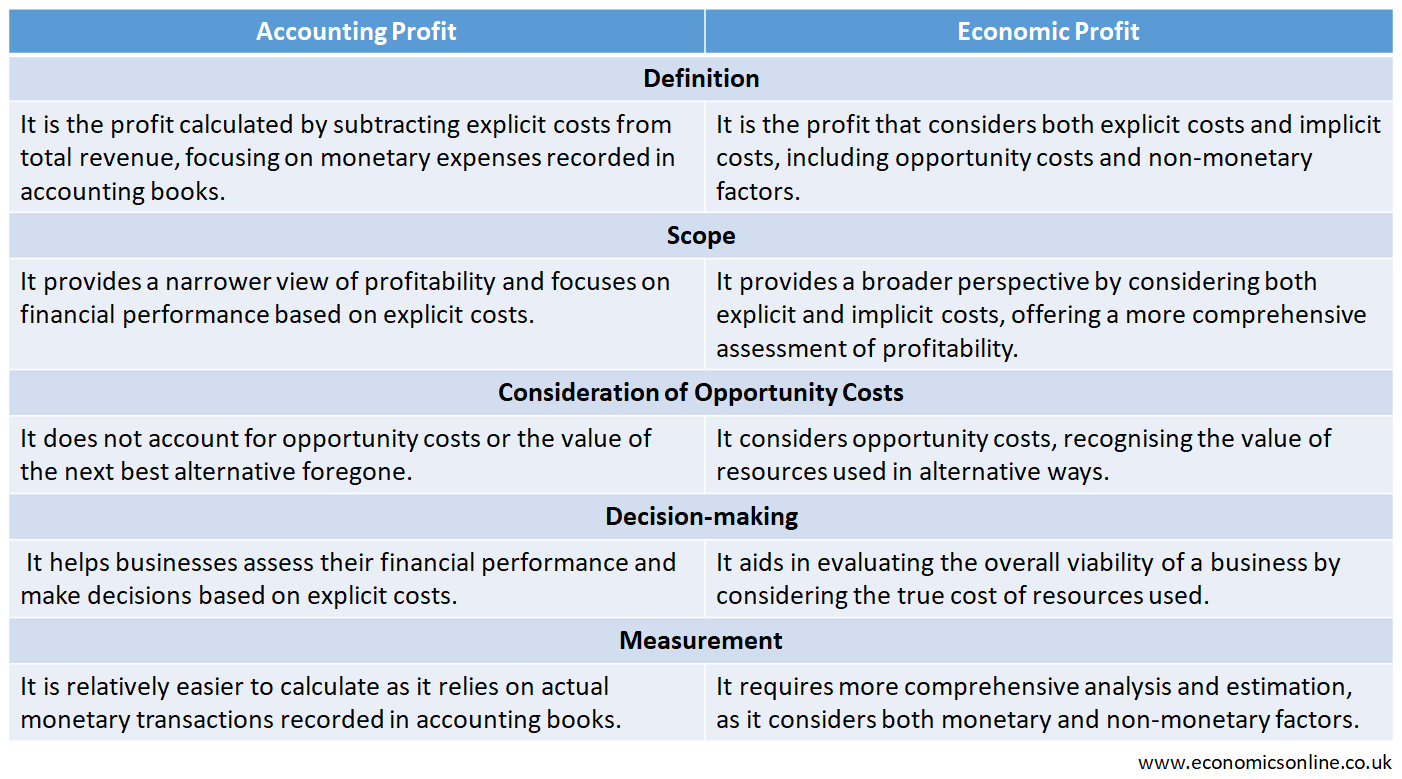
Difference between Accounting Profit and Economic Profit
The following table summarises the main points of difference between accounting profit and economic profit.
Understanding Accounting and Economic Profits with Calculation Examples
Let’s understand the concepts of accounting profit and economic profit with the help of calculation examples.
Suppose that a business has earned total revenue of $40000 and its explicit cost is $15000 for the same time period. Here,
Total Revenue = $40000
Explicit Cost = $15000
We can easily calculate the accounting profit as follows:
Accounting profit = Total Revenue – Explicit Cost
Accounting Profit = $40000 - $15000 = $25000
Now, suppose that the implicit cost (opportunity cost) is $13000. The economic cost can be calculated as follows:
Economic Cost = Explicit Cost + Implicit Cost
Economic Cost = $15000 + $13000 = $28000
Now we can calculate economic profit as follows:
Economic Profit = Total Revenue – Economic Cost
Economic Profit = $40000 - $28000 = $12000
Since this economic profit is positive, it is called abnormal profit or supernormal profit.
Importance of Implicit Costs
The importance of implicit costs is explained as follows:
Opportunity Cost
Implicit cost is the opportunity cost of making a decision, and it is considered an expense in economics.
Profit Calculation
By considering explicit costs along with implicit costs, a comprehensive calculation of economic profit is made. This helps in evaluating different options when making decisions about resource allocation.
Decision-making
Implicit cost allows us to make informed decisions by identifying opportunity cost. Individuals and firms can make better decisions in which not only explicit costs are considered but also implicit costs are included for all the available options. This will improve the quality of decision making.
Resource Allocation Efficiency
Individuals and firms consider various options of resource allocation and evaluate them in a better way by considering implicit costs. This helps the business firms in improving efficiency in resource allocation.
Importance of Explicit Costs
The importance of the explicit costs is explained as follows:
Financial Accountability
Explicit costs are recorded in the books of accounts. This helps the business to keep the accurate record of all the expenses incurred and hence provide financial accountability.
Profit Calculation
Profit calculations are critical for any business in assessing its financial performance. The explicit costs are used to calculate accounting profits which give a good indication of the financial performance of a business.
Cost Control
By keeping the record of the explicit costs, businesses can control costs. This will improve business efficiency and profits.
Pricing and Budgeting
Explicit costs help business firms in making pricing decisions for their products and budget for their operations. Setting the right price and making use of budgets is important for improving business performance.
Compliance
Explicit costs provide compliance along with accounting standards and reporting information, which provide accurate information to stakeholders in their business.
Importance of Accounting Profit
The importance of the accounting profit is explained as follows:
Performance Evaluation
Accounting profit is used to evaluate the financial performance of a business for a specific period of time. This helps various stakeholders in making better financial decisions.
Investor Confidence
Investors consider the values and trends in accounting profits in making investment decisions. A business showing an increasing trend of the accounting profit gives its investors the confidence for making investment decision in its favour.
Taxation and Compliance
Accounting profit helps to calculate taxes and provide compliance with financial performance and regulations.
Importance of Economic Profit
The importance of economic profit is explained as follows:
True Measure of Performance
Economic profit goes beyond accounting profit by considering both explicit and implicit costs, providing a more accurate measure of a business's overall financial performance.
Opportunity Cost
While calculating true economic profit, we use economic cost in which opportunity cost or implicit cost is also included. This helps the businesses in evaluating the true value of alternative uses of resources and hence, better decisions can be made.
Long-Term Viability
Economic profit helps assess the long-term sustainability of a business by considering all costs, including foregone opportunities, and determining if the business is generating enough profit to cover all expenses.
Resource Allocation Efficiency
By considering economic profit, businesses can allocate resources more efficiently, focusing on activities that generate the highest returns after the consideration of all the costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implicit cost is the opportunity cost of making a decision. This cost is not recorded in financial statements of a business, yet they are considered vital for making decisions. On the other hand, explicit costs are the actual expenses that are incurred in a business when producing goods or services. These are out-of-pocket costs. These costs are recorded in the books of accounts are vital in cost control, financial efficiency, pricing, and profit calculations. These costs include costs of inputs used in production, office rental, cost of utilities, marketing expense and other monetary transactions. Both of the definitions of cost are important in understanding two different conceptions of profit, however, the consideration of implicit costs in decision making is a major advantage of economics over other subjects.


