
An image of web network
Quaternary Sector
Introduction
An economy is an area where goods and services are produced to satisfy the needs and wants of people. To understand an economy in a better way, we divide it into different broad groups of firms called sectors. These sectors are the primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, and quinary sectors. In this article, we will explore the meaning, characteristics, and some other details of the quaternary sector of the economy. But first, let us understand some basic terms.
Basic Terms
Industry
An industry refers to the collection of similar types of business firms. It is a specific segment of business firms involved in similar economic activities. For example, the education industry is composed of all the schools, colleges, and universities providing educational services.
Sector
A sector refers to a broad collection of business firms based on the nature of the economic activity they perform. A sector may contain business firms from many industries. For example, the primary sector is composed of business firms that are involved in the extraction of natural resources, like mining firms, agricultural farms, fish farms, and so on. Economists divide the economy into different sectors so that they can understand, analyse, and compare the contribution of different sectors towards the whole economy in terms of output and job creation.
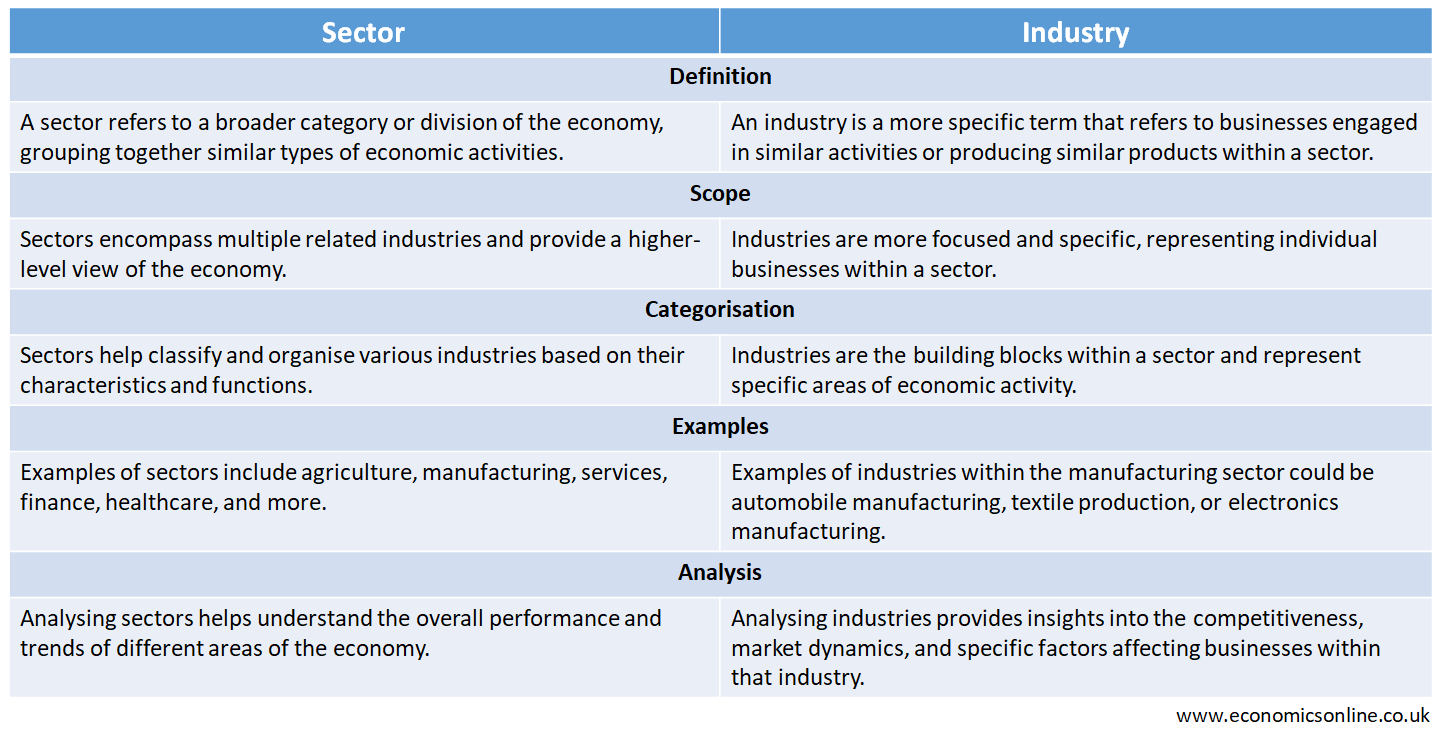
Difference between Sector and Industry
The following table summarises the main points of difference between a sector and an industry.
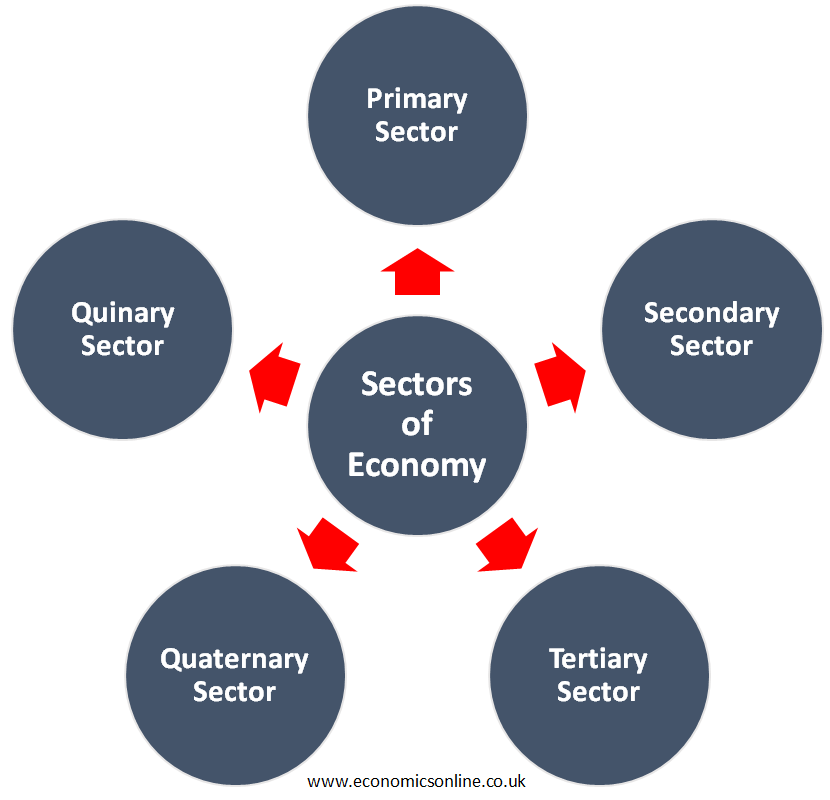
Types of Sectors of Economy
Traditionally, economists divided the economy into three main sectors, which were the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors. However, due to the increasing contribution of information-based businesses towards job creation and economic growth, economists now consider five sectors of the economy, which are explained below:
Primary Sector
The primary sector of the economy refers to the collection of business firms that are involved in the extraction of natural resources. Some examples of business activities in this sector are fishing, mining of gold, oil extraction, agriculture, etc. In poor countries, the primary sector has the highest contribution to the country’s output and employment.
Secondary Sector
The secondary sector of the economy refers to the collection of business firms that are involved in transforming raw inputs into finished goods. This sector is also called the manufacturing sector. Some examples of business activities in this sector are construction, automobile manufacturing, garment manufacturing, and so on. An increase in the secondary sector of the economy is called industrialization, while its decrease is called de-industrialisation. In many developing economies, the secondary sector has the highest contribution to the country’s output and employment.
Tertiary Sector
The tertiary sector of the economy refers to the collection of business firms that are involved in providing services. Some examples of business activities in this sector are retailing, banking, education, legal consulting, and so on. In many developed economies, the tertiary sector is dominant and has the highest contribution to the country’s output and employment.
Quaternary Sector
The quaternary sector of the economy refers to the collection of business firms that are involved in knowledge-based activities that are focused on intellectual capital. Some examples of business activities in this sector are research and development, information and communication technology (ICT), financial consulting, and so on. Some experts consider this sector a sub-set of the tertiary sector. However, some other experts consider it a separate sector due to its increasing contribution to the country’s output and employment.
Quinary Sector
The quinary sector of the economy refers to the part of the economy where high-level decisions are made by top-level officials, leaders, and top executives in government, industry, and non-profit organisations. This sector also includes important and strategic organisations like defense, public services, healthcare, and education. Some experts consider this sector an extension of the tertiary sector of the economy.
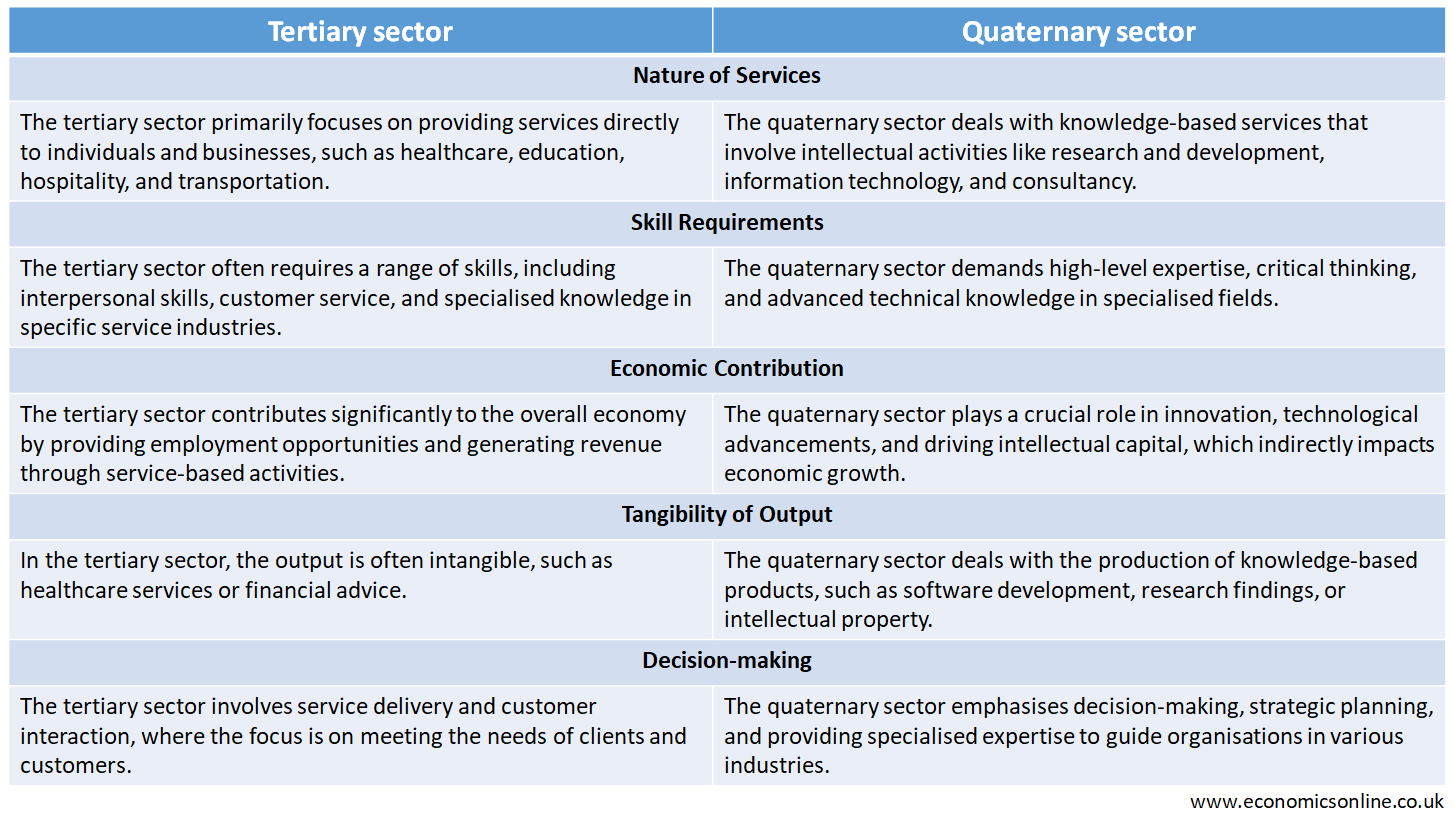
Difference between Tertiary Sector and Quaternary Sector
The following table summarises the main points of difference between the tertiary sector and the quaternary sector.
The Emergence of Quaternary Sector
Traditionally, economists like Allan Fisher, Colin Clark, and Jean Fourastié believed in the three-sector model of the economy. These three sectors were the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors. However, due to the rise in information-based economic activity, a fourth sector (quaternary sector) emerged. This idea is illustrated by the following graph.
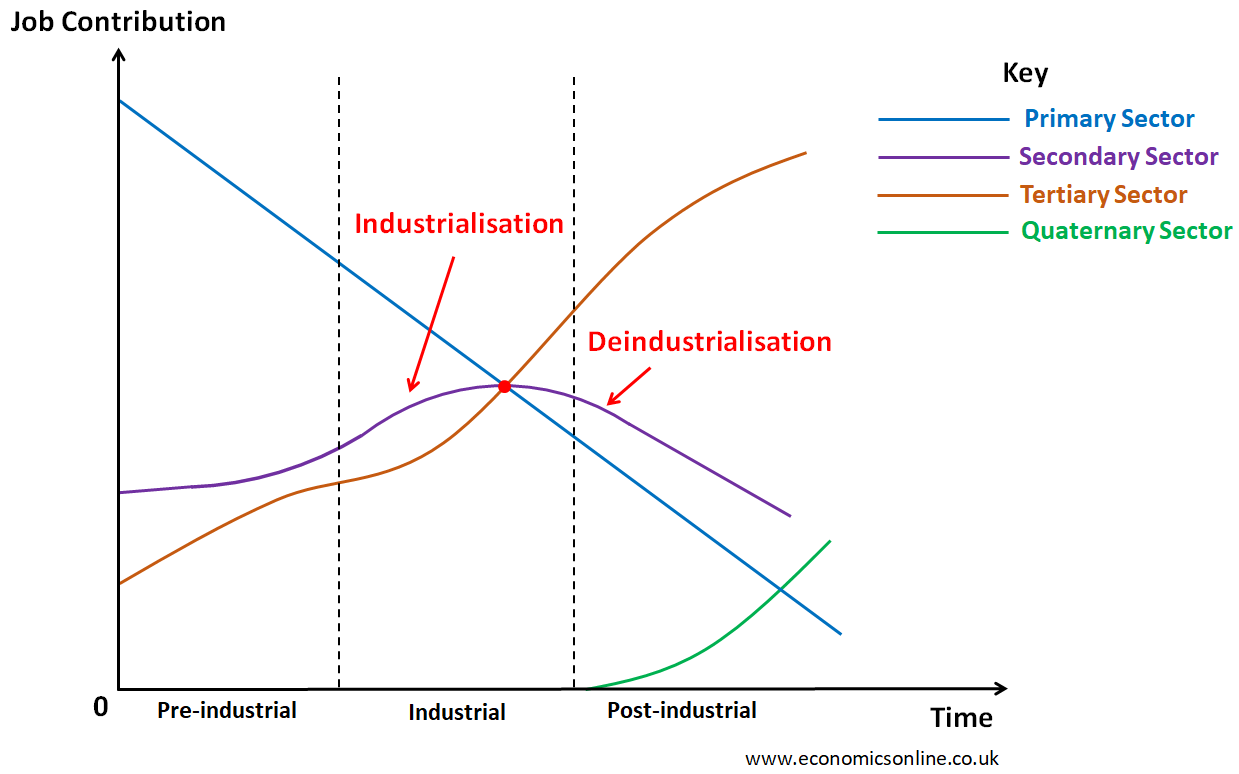
In the above graph, the horizontal axis (x-axis) is labeled with time and the vertical axis (y-axis) is labeled with job contribution. The graph has three parts:
Pre-Industrial Phase
This is the first stage of economic development and some poor countries are in this stage. The primary sector of economy is dominant in terms of job creation.
Industrial Phase
This is the second stage of economic development and countries go through the rise in secondary sector in the form of industrialisation. Some developing countries are in this stage where the secondary sector is dominant in terms of job creation and country’s output.
Post-industrial Phase
This is the third stage of economic development and countries go through the rise in tertiary sector and deindustrialisation. Quaternary sector also emerge in this stage. Many developed countries are in this stage where the tertiary and quaternary sectors contribute more in terms of job creation and country’s output.
One should not perceive from the above graph that the quaternary sector is only present in the developed countries. While it is true that the quaternary sector is highly visible in developed countries, many developing countries also have quaternary activities.
Quaternary Sector Examples
Quaternary sector businesses are involved in specialised tertiary activities which are knowledge-based. Some examples of such activities are:
Software development, data analysis, research and development (R&D), biotechnology, telecommunication services, research work, aerospace research, cyber-security services, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), financial technology (FinTech), information technology (IT), robotics, internet of things, big data, telemedicine services and intellectual property laws. Software development companies like Apple and Microsoft, research firms like NASA and financial service companies like Goldman Sachs are the some examples of the quaternary sector businesses in the United States.
Characteristics of Quaternary Sector
The following are some main characteristics of the quaternary sector:
Knowledge-based Economy
The quaternary sector provides a knowledge-based economic system that includes cognitive activities such as research, innovation, development, and information services.
High Skill Requirements
Some jobs in the quaternary sector require high skills and expertise, such as advancement education in specific fields of technology, finance and research.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancement is one of the main characteristics of the quaternary sector. This is important for innovating new products and improving the existing products for the growth business firms and the economy.
Intellectual Capital
The generation of intellectual capital is done with the help of technological advancement in the quaternary sector, which provides information to compete with other businesses and stimulates economic growth.
Global Nature
Due to the global nature of the quaternary sector, businesses can compete, collaborate, share knowledge and provide services to their clients across country borders.
Purpose of Quaternary Sector
The main purpose of the quaternary sector is to provide knowledge-based economic services, make intellectual capital, and drive technological advancement for each manufacturing and service sector of a country. The quaternary sector provides information and knowledge for conducting research with the help of high skills and expertise.
Advantages of Quaternary Sector
The following are the advantages of the quaternary sector:
High Skill Employment Opportunities
The quaternary sector provides high-skill employment opportunities to students by providing knowledge and expertise.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The quaternary sector creates technological advancements and innovation in the manufacturing and service sectors of a country.
Diversification
The quaternary sector contributes to the diversification of the economy to enhance economic growth in a country.
Resilience
The quaternary sector provides flexibility during economic instability and inflation.
Market Opportunities
The quaternary sector expands market opportunities for industries operating on a global level.
Quaternary Sector and Workforce Transformation
The transformation of the workforce in the quaternary sector is explained as follows:
Skills Requirements
The quaternary sector demands high skills and knowledge; this will shift the trend toward a more educated and technically sound workforce.
Remote Work and Digital Collaboration
The advancement in technology can enable the remote work and digital collaboration opportunities for individuals interested in remote jobs and work-from-home jobs on a global scale.
Gig Economy and Freelancing
The gig economy and freelancing are increasing day by day, which provides flexibility and the potential for professionals to work on many projects at a time.
Interdisciplinary Approach
In quaternary sectors, professionals use an interdisciplinary approach. This approach encourages those people to solve complex problems and do research at a high level of skill.
Lifelong Learning and Continuous Skill Development
The continuous evolution in the quaternary sector allows individuals to engage in lifelong learning and skill development to stay relevant to the industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, technological advancement is the key role that quaternary sector perform. Quaternary sector is helpful for the workforce to become that much capable of getting a high paid job according to their own benefit. The quaternary sector also provides benefit to the industries working at a global level.

